Середина цикла болит низ живота: Почему болит живот в середине цикла, как перед месячными
С периодическими болями внизу живота знакома каждая женщина. Появляются перед месячными либо во время менструации. Часто женщины жалуются, что в середине цикла болит живот. Тянущая боль возникает по ряду причин, основная – наступление овуляции.


Овуляция происходит каждый месяц. В этот момент яйцеклетка выходит из яичника. Период созревания яйцеклетки считается благоприятным моментом для зачатия ребёнка. Регулярный менструальный цикл зависит от времени и наличия овуляции.
Статистика показывает, что большинство представительниц прекрасного пола не знают, когда наступает момент выхода яйцеклетки. У здоровой женщины это обычно середина цикла. В упомянутый период повышается базальная температура тела. Появляются незначительные боли внизу живота, набухание молочных желез. Для уточнения начала овуляции рекомендуют сделать специальный тест (продаётся в аптеке).
Боль при овуляции
Болевые ощущения в животе при овуляции возникают из-за разрыва фолликула яичника, зрелая яйцеклетка высвобождается. Процесс высвобождения длится несколько минут. Но ощущения способны продолжаться до нескольких суток. Причина тому – разрыв кровеносных сосудов и незначительное кровотечение.
Локализация боли зависит от расположения яичника, откуда вышла яйцеклетка. Носит разнообразный характер: бывает тянущей либо острой. На продолжительность болевого ощущения влияют:
- Наличие спаек маточных труб;
- Рубцы;
- Эндометриоз;
- Воспаления в органах малого таза.

Выявить причину появления болей в середине цикла способен исключительно гинеколог.
Диагностика боли
Установить точный момент, когда яйцеклетка покинет яичник, трудно. Женщине потребуется некоторое время наблюдать за собственным организмом, измерять базальную температуру.
Измеряют её сразу после пробуждения. Ртутный градусник вставляют в анальное отверстие. До овуляции температурная норма составляет 36,4-36,7. В момент выхода яйцеклетки температура повысится до 37-37,3 градусов, продержится до начала следующих месячных. Метод позволяет точно определить день начала овуляции. Для подстраховки рекомендуют сделать тест.
Важно установить длительность менструального цикла. Считается от первого дня месячных до наступления следующих. Длина цикла каждой женщины индивидуальна. Нормой считается продолжительность 28 – 35 дней.
Овуляция сопровождается симптомами:
- Скачки настроения;
- Увеличение сексуального желания;
- Обильные прозрачные выделения из влагалища;
- Тяжесть в молочных железах.
Медикаментозного лечения овуляция не требует. Незначительное болевое ощущение – нормальный процесс. В этот период рекомендуется пить больше жидкости, гулять на свежем воздухе, чаще кушать овощи и фрукты, избегать стрессов и сильных эмоциональных нагрузок.
Возможные причины
Отсутствие либо пропуск овуляции сказывается на менструации. Нормальным считается пропуск два-три раза в год. С рождения у женщины закладывается определённое количество яйцеклеток. По мере снижения репродуктивной функции количество сокращается. Месячные идут, но скудно.
Если овуляция отсутствует в фертильном возрасте женщины, это указывает, что нарушена репродуктивная система. Последствием может стать бесплодие либо неспособность выносить ребёнка. Если выход яйцеклетки не наступает на протяжении двух-трёх месяцев подряд, полагается обратиться к врачу. Проведя исследования, гинеколог выявит причины овуляторной дисфункции.
Увеличение уровня эстрогена
Тянуть низ живота в середине цикла может из-за низкого уровня эстрогена. Деятельность матки и чувствительность женщины напрямую зависят от гормонов. Максимальное увеличение эстрогена наблюдается у женщин ближе к 40 годам. В этот период месячные сопровождаются особенно сильными болевыми ощущениями.
Изменение гормонального фона становится причиной возникновения ПМС и альгодисменореи (болит поясница, появляются резкие боли внизу живота). Начинаются головокружения и тошнота, слабость. Для облегчения состояния рекомендуют выпить анальгетики.
Повышенный уровень простагландинов
Появление болей – основной признак высокого уровня простагландинов. Из-за их повышения происходит сбой в гормональном фоне. Сопровождается болевыми ощущениями в спине и пояснице при месячных.

Назначение простагландинов – приводить к сокращениям матки при родах. Ферменты вырабатываются в матке. При созревании фолликула повышают давление, он разрывается. Поэтому в середине менструального цикла возникают схваткообразные боли.
Гинекологи называют процесс овуляторным синдромом. Часто сопровождается головной болью, учащённым сердцебиением, тошнотой, ознобом и рвотой.
Причиной синдрома может стать инфекционное заболевание, отчего происходит воспалительный процесс в яичнике. Его стенки уплотняются, выход яйцеклетки затруднен. Чтобы яйцеклетка вышла, требуется большое давление на фолликул. Так происходит травмирование сосудов.
Увеличение щитовидной железы
За работу и создание гормонов в организме человека отвечает щитовидная железа. При её увеличении нарушается гормональный фон. Во время месячных женщина испытывает болевые синдромы, появляется бессонница.
Увеличение щитовидной железы приводит к нарушению работы всего организма. В матке и во влагалище происходят патологические воспалительные процессы. Возникают инфекционные и бактериальные заболевания, миома матки, эндометриоз.
Применение внутриматочных контрацептивов
Внутриматочные контрацептивы способны стать причиной боли в средине цикла. Болевые ощущения вызваны наличием инородного тела. Также синдром порой спровоцирован синтезом простагландинов.
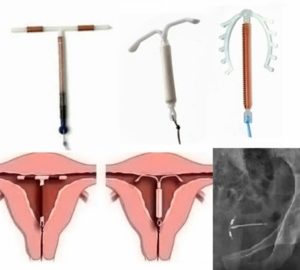

Если боли возникают часто, лучше отказаться от внутриматочной спирали. Обращение к врачу требуется, если:
- На протяжении всей менструации присутствуют резкие тянущие боли в области живота и поясницы.
- Болевые ощущения усиливаются и не проходят дольше 2 дней.
- Синдром сопровождается дискомфортом, зудом, жжением половых органов. Мочеиспускание сопровождают резкие боли. У влагалищных выделений появился резкий запах.
- Возникло сильное кровотечение при месячных (за час прокладка наполняется полностью).
- Повышение температуры на фоне воспалительного процесса.
Возможная беременность
Причиной тянущих болей после овуляции бывает беременность. После оплодотворения яйцеклетка крепится в стенку матки. В этот период появляются боли внизу живота, которые напоминают болевой синдром как в дни перед месячными. На ранних сроках беременности болит та сторона, откуда вышла яйцеклетка.
- Синдром появляется из-за повышенного кровообращения в матке. С кровью к эмбриону поступает кислород и питательные вещества. Но усиленное кровообращение повышает тонус матки, последствием станет самопроизвольный выкидыш либо его угроза.
- Тянущие болевые ощущения появляются из-за смягчения и растяжения тканей и связок матки. Происходит её увеличение и смещение. Быстрый рост происходит в первые месяцы беременности. Как правило, ко второму триместру синдром пропадает.
- Причиной появления боли становится повышенный уровень прогестерона. При этом ощущение распространяется на ноги, спину, поясницу.
Чтобы не спутать беременность с болезнями, женщина должна прислушаться к собственному телу. Как только произошло зачатие, организм будущей мамы готовится к рождению ребёнка. Грудь начинает увеличиваться и болеть при любых прикосновениях к ней.
Визит к врачу
Консультация врача необходима, если боли продолжаются долгое время. Сложность заключается не только в овуляции и в патологии органов малого таза. Живот болит из-за заболеваний ЖКТ, аппендицита и ряда других болезней.
При лечении болей в средине цикла полагаться на обезволивающие препараты не стоит. Их действие нацелено на снятие симптома. Если болезненность появляется на протяжении двух-трёх циклов, пора показаться гинекологу. Врач назначит необходимые анализы и исследования.
Незамедлительный поход потребуется, если женщина обнаружила у себя один либо несколько симптомов, сопровождающих болевые ощущения: тошноту, рвоту, слабость, резкое повышение температуры, зуд и жжение половых органов.
почему возникает боль внизу, причины
Нередко женщины обращаются к врачу с жалобами на то, что у них болит живот в середине цикла. Причиной тому могут стать физиологические процессы в женском организме, например, наступление овуляции, но иногда они могут свидетельствовать о наличии патологического процесса.
Боль – это не заболевание, это защитный механизм нашего организма, который сигнализирует о наличии развивающегося патологического процесса. Одни люди легче переносят боль, другие же более чувствительные. Крайне важно установить истинную причину своего состояния, в этом поможет квалифицированный специалист.
В первую очередь специалист обращает внимание на характер болевых ощущений. Приступ может быть слабым, умеренным или интенсивным. Болевая вспышка может носить временный характер или беспокоить женщину постоянно.
Важно установить существует ли взаимосвязь с менструальным циклом. Возможно, болезненность сигнализирует о наступлении овуляции. Кроме того, следует установить взаимосвязь боли в животе с мочеиспусканием, актом дефекации и приемом пищи.
Женские причины
Почему болит живот в середине цикла? В зависимости от локализации боль в животе может быть односторонней (справа или слева), двусторонней или разлитой. Причины болевой вспышки делятся на физиологические и патологические. К физиологическим факторам относят стрессовые ситуации, предменструальный период, беременность, переохлаждение, период овуляции, изменение половой активности.
На ранних сроках беременности матка еще не достигла таких размеров, чтобы кости таза ее поддерживали, поэтому вся нагрузка приходится на связки. Сдавливание близлежащих рецепторов и провоцирует появление болевого синдрома. Боль нарастает постепенно и имеет маловыраженный характер.
На появление болезненности могут влиять и возрастные особенности. Так, в подростковые годы менструальный цикл часто бывает нестабильным. Критические дни могут наступить на две недели раньше или позже. В таком случае у девушки боли могут быть связаны с наступлением менструации, а она думает, что до нее еще очень далеко.
Боли внизу живота в середине цикла могут возникать на фоне таких патологических процессов, как:
- цистит;
- сальпингоофорит;
- эндометрит;
- альгодисменорея;
- заболевания яичников;
- аппендицит;
- эндометриоз;
- венерические заболевания;
- пиелонефрит;
- дивертикулит;
- спаечное заболевание;
- заболевания кишечника.

Боль в животе в середине цикла может возникать на фоне стрессовых ситуаций
Овуляция
Появление тянущих болей внизу живота при наступлении овуляции обусловлено разрывом тонкой оболочки фолликула, выходящего из яичника. Это происходит каждый месяц и является показателем репродуктивного здоровья женщины.
Считается, что овуляция происходит в середине менструального цикла, однако иногда рождение зрелой яйцеклетки может происходить в начале или даже в конце цикла. Это может быть связано с некоторыми факторами:
- состояние здоровья;
- переезд;
- перепад температуры;
- стрессовые ситуации;
- физические нагрузки;
- интенсивность полового акта.
В этом случае болевая вспышка может длиться от нескольких часов до двух-трех дней. При половом акте болезненные ощущения, как правило, усиливаются. Болевой синдром при овуляции возникает из-за растяжения связок в области яичников. Также боль вызывает разрыв фолликула яичника при высвобождении яйцеклетки.
Это вызывает повреждение кровеносных сосудов и небольшое кровотечение. При этом стоит отметить, что сам выход яйцеклетки длится всего несколько минут. Болевой синдром при овуляции в большинстве случаев носит односторонний характер, из-за чего женщина может подумать, что у нее проблемы с яичниками.

Низ живота может болеть при овуляции, которая обычно наступает за две недели до месячных. Также часто болит и грудь
Болезненные ощущения могут появляться слева или справа. Это зависит от того, какой яичник продуцирует яйцеклетку. Специалисты утверждают, что правый яичник работает более интенсивно по сравнению с левым. Болевой синдром приобретает тянущий характер, а иногда переходит в острые приступы.
Одни женщины говорят, что ноющую боль можно терпеть, другие же жалуются на сильные невыносимые боли.
Выраженный болевой синдром в период овуляции может указывать на повышенный уровень простагландинов. Это вызывает так называемый овуляционный синдром. Суть патологического процесса связана с повышением давления внутри созревшего фолликула, из-за чего происходят постоянные его разрывы и кровотечения в брюшину. В этом случае боль может отдавать в копчик и поясницу.
Гормональный сбой
Всеми процессами в женском организме управляют именно гормоны. Прогестерон и эстроген отвечают за половое созревание и наступление менструации, а также в целом за функционирование всей репродуктивной сферы.
Именно поэтому гормоны должны находиться в определенном балансе. Уменьшение или увеличение женских гормонов сказывается на самочувствии женщины, ее внешнем виде и функционировании внутренних органов. Гормональный дисбаланс может возникнуть даже в молодом возрасте.
Для него характерно появление следующих симптомов:
- нарушение менструального цикла. Сюда можно включать альгодисменорею – болезненные месячные, задержку, скудные или, наоборот, кровянистые выделения крови, а также выраженные проявления предменструального синдрома;
- кровотечение;
- проблемы с зачатием;
- усталость и раздражительность;
- бессонницы;
- головокружение и головные боли;
- увеличение веса;
- скачки давления и другое.

Гормональный сбой – это распространенная причина болей
Причиной такого нарушения могут стать постоянные стрессовые ситуации, неправильное питание, прием гормональных средств, лишний вес, интенсивные физические нагрузки. Поставить точный диагноз помогут анализы на гормоны. Гормональный дисбаланс – это достаточно серьезно нарушение, которое может привести к бесплодию, развитию злокачественных новообразований, инфарктам, инсультам.
Эндометриоз
Заболевание характеризуется разрастанием эндометрия – внутреннего слоя матки. Спровоцировать появление патологического процесса могут регулярные инфекционно-воспалительные процессы репродуктивной сферы, ослабленный иммунитет, эндокринные нарушения, вредные привычки, осложненные роды, оперативное вмешательство.
Эндометриоз в некоторых случаях протекает бессимптомно. Заболевание не отличается наличием специфических признаков, все же заподозрить развитие процесса можно по следующим симптомам:
- болит низ живота в середине цикла. Неприятные ощущения часто отдают в пах и поясницу;
- болезненные продолжительные месячные с обильными выделениями крови;
- бесплодие.
Вагинит
Вагинит – это заболевание, при котором воспаляется слизистая оболочка влагалища. Причиной развития недуга часто становится проникновение болезнетворных микроорганизмов. Женщины жалуются на появление зуда, жжения и ощущения распирания в области наружных половых органов.
Если возбудителем вагинита стала гонорейная инфекция, появляются гнойные густые выделения бело-желтого цвета. При трихомонадном поражении появляются желто-зеленые выделения пенистой консистенции. Для бактериального вагинита характерны бело-желтые обильные влагалищные выделения. О грибковой инфекции свидетельствуют творожистые рыхлые выделения.
Лечение включает в себя применение общих и местных средств. Терапию должен пройти и половой партнер.
При вагините болезненность сопровождается появлением патологических выделений
Другие причины
Не всегда болезненность вызывают гинекологические проблемы. Причиной может стать аппендицит и цистит. Поговорим подробнее об этих заболеваниях.
Аппендицит
Это одна из распространённых хирургических патологий органов пищеварения. Опасность заболевания связана с рисками возникновения опасных осложнений. Аппендицит может возникнуть у человека в абсолютно любом возрасте. Согласно статистике, женщины страдают чаще, чем мужчины.
В основу заболевания ложится воспаление червеобразного отростка слепой кишки. По мере развития патологического процесса орган увеличивается в размерах и становится болезненным. Это приводит к разрыву стенок червеобразного отростка и выходом гнойного секрета наружу.
Причины аппендицита до сих до конца не изучены. Все же специалисты выделяют некоторые теории в возникновении воспалительной реакции. Закупорка червеобразного отростка каловыми массами, бактериальная инфекция, спазм сосудов, травма живота, склонность к запорам – все это и многое другое может привести к появлению аппендицита.
Заболевание вызывает острый приступ боли, повышение температуры, тошноту, рвоту. Сначала боль имеет разлитой характер и возникает в верхней части живота, а через несколько часов перемещается в правый нижний бок.

При аппендиците появляется резкая боль в животе
Цистит
Цистит – это инфекционно-воспалительное заболевание стенок мочевого пузыря. Мочеиспускательный канал у женщин более широкий и короткий, поэтому они страдают циститом чаще, чем мужчины. Основной причиной заболевания являются бактерии. Тянущие боли в надлобковой области сопровождаются болезненным и учащенным мочеиспусканием, помутнением мочи.
В некоторых случаях повышается температура, а также появляется тошнота и рвота. Больным показан постельный режим. Ведущим принципом лечебного процесса является борьба с бактериальной инфекцией. Для купирования неприятных симптомов назначаются препараты на основе трав.
Боль и коричневые выделения
Для начала поговорим о физиологических причинах, при которых появление коричневых выделений считается вариантом нормы:
- приближение менструации;
- избавление матки от лишних капель крови после окончания месячных;
- прием оральных контрацептивов;
- бурный половой акт;
- начало половой жизни.
К сожалению, не всегда коричневые выделения являются нормой. В некоторых случаях они являются симптомом серьезных патологий. На это могут указывать такие признаки:
- кровянистые выделения появляются в середине цикла, при этом женщина не принимает контрацептивы;
- появление болей, чувства жжения, зуда, сухости во влагалище, неприятных ощущениях при половом контакте;
- уже более года отсутствуют месячные по причине менопаузы;
- постоянные выделения после полового акта.
Маточное кровотечение вызывает боль внизу живота
Теперь поговорим о патологических причинах коричневых выделений. Специалисты выделяют две основные причины: маточное и межменструальное кровотечение. Первая причина возникает на фоне заболеваний матки: эндометрита, фибромы, саркомы, эрозии и рака шейки матки.
Межменструальные кровотечения могут возникнуть вследствие таких причин: влияние гормональных контрацептивов, эндокринные нарушения, заболевания, передающиеся половым путем, гормональный дисбаланс, стрессовые ситуации.
Итак, живот может болеть в середине цикла по целому ряду причин – как физиологических, так и патологических. Зачастую это связано с наступлением овуляции или гормональным сбоем. Вызвать болезненность могут такие заболевания, как аппендицит, цистит, вагинит, эндометриоз. Определить истинную причину сможет врач после прохождения обследования.
Боли в животе в середине цикла: причины :: SYL.ru
Менструальный цикл является информативным способом определить, здорова ли женщина. В зависимости от того, насколько регулярно идут месячные, как долго длятся, болезненные они или нет, врачом-гинекологом выявляются различные патологии.
Середина цикла, или овуляция, у большинства женщин протекает бессимптомно. Лишь малая часть прекрасной половины человечества испытывает неприятные ощущения, а иногда – сильную боль в животе именно в это время.
Являются ли боли в животе в середине цикла нормой, разберемся в данной статье.
Что такое овуляция?
Продолжительность менструального цикла у женщины рассчитывается от того дня, когда начались предыдущие месячные, до того дня, когда закончились следующие. Нормой считается цикл в 21-34 дня. Лунным циклом считается период в 28 календарных дней, это является классическим вариантом нормы. Почему в середине менструального цикла болит живот?
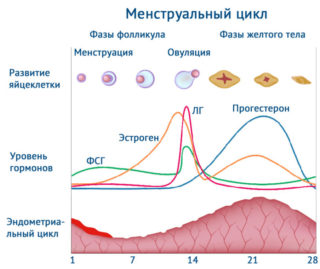
Фазы менструального цикла
Женский цикл делится на несколько фаз:
– фолликулярную;
– овуляторную;
– лютеиновую.
В фолликулярную фазу цикла созревает яйцеклетка в одном из яичников, в котором образуется доминантный фолликул. Этому процессу помогают женские половые гормоны эстрогены. Длится эта фаза в среднем 2 недели, но у каждой женщины по-разному. Иногда больше дней, иногда меньше. Когда фолликулярная фаза завершается, фолликул полностью созрел и должен лопнуть.
При овуляторной фазе, являющейся самой непродолжительной, эстрогены в женском организме уменьшаются. В результате чего фолликул разрывается, а яйцеклетка перемещается по маточной трубе. Гормон прогестерон также находится на низком уровне. Длительность овуляторной фазы – максимально 36 часов. Именно в это время возникают боли в животе в середине цикла.
Во время следующей, лютеиновой фазы значительно увеличивается количество прогестерона в организме женщины. Это помогает слизистой матки подготовиться к закреплению яйцеклетки. Но поскольку зачатия не происходит, то прогестерон прекращает выработку. В результате этого происходит отторжение верхнего слоя слизистой матки, который носит название эндометрий. Этот процесс отторжения и называется менструацией.
Как стало понятно из вышеизложенного, непосредственно разрыв фолликула и процесс выхода яйцеклетки является овуляцией. При этом боль, которую испытывает женщина в середине цикла, является вариантом нормы. Это так называемый синдром Миттельшмерца, или овуляторный синдром.
Разберемся, в каких случаях женщине волноваться не нужно, а когда следует незамедлительно обратиться к врачу.
Как определить начало овуляции?
Боли в животе в середине цикла бывают довольно часто.
Есть определенные симптомы, которые могут помочь женщине выявить начало овуляторной фазы. Рассмотрим их более подробно:
– боль в боку или внизу живота;
– сильное половое влечение;
– изменение характера выделений;
– болезненные ощущения в молочных железах.
Болезненные ощущения внизу живота, чаще всего боль локализуется в каком-то одном боку. Левый это бок или правый, зависит от того, в каком яичнике располагается доминантный фолликул. У некоторых женщин сильнее боль проявляется с правой стороны, поскольку правый яичник ближе к аппендиксу, а также он лучше снабжается кровью. Насколько сильна боль? В основном это легкий дискомфорт. Но в определенный момент времени боль достигает своего апогея и ощущается как схватки, рези. В боку, где расположен активный яичник, может сильно колоть, иногда нестерпимо. Но важно понимать, что при овуляции болевые ощущения не должны быть слишком долгими. Продолжается она несколько часов, максимум сутки. Вот почему болит живот в середине цикла.
От чего может зависеть интенсивность боли?
Прежде всего от восприимчивости и чувствительности женщины. Также при наличии гинекологических заболеваний болезненность всех процессов усугубляется.
Важно отметить, что в редких случаях созревание яйцеклетки наблюдается в обоих яичниках. Если бы произошло оплодотворение, то у женщины наступила многоплодная беременность. А при овуляции боль не локализуется в одном боку, а «разливается» внизу живота. Так проявляются боли в животе в середине цикла.
Почему повышается либидо в середине цикла? Это состояние является закономерным, поскольку овуляция – наилучшее время для зачатия.
Характер выделений из половых путей видоизменяется – они становятся абсолютно прозрачными, как яичный белок. Это позволяет сперматозоидам легче проникать в полость матки женщины. В редких случаях в выделениях имеется кровь, но в очень небольшом количестве. Это происходит по причине отслойки небольшой эндометрия в результате прекращения выработки эстрогена и прогестерона одновременно.
Болезненность груди бывает в результате гормональной перестройки организма женщины, то есть молочные железы начинают подготовку к процессу кормления будущего малыша. Но этого может и не наблюдаться. А чаще всего болит низ живота в середине цикла.
Виды отклонения от нормы
Специалисты разделяют овуляцию на три вида. Она может быть у женщины своевременной, преждевременной и поздней.
Преждевременно яйцеклетка может выйти из яичника по нескольким причинам:
– в результате слишком активного полового контакта;
– по причине сбоя в работе гормональной системы организма;
– интенсивных физических упражнений;
– по болезни;
– в результате сильного нервного перенапряжения.
Запаздывать овуляция может ровно по тем же причинам. Поэтому не стоит слишком пугаться, если боль началась раньше середины цикла или, наоборот, позже. Но чаще болит живот в середине цикла. Причины рассмотрим далее.
Ановуляция
В некоторые месяцы овуляция может полностью отсутствовать у женщины. Это происходит редко. В норме овуляторной фазы цикла не бывает при наступлении беременности, в климакс, а также тогда, когда женщина принимает оральные контрацептивы.
Если овуляции нет более двух месяцев подряд, следует обязательно получить консультацию у гинеколога. Особенно серьезно следует к этому относиться тем женщинам, которые планируют стать матерью.
При помощи современных методов можно определить точную дату овуляции. Имеются специальные тесты, также это можно сделать на УЗИ (там будет хорошо виден увеличенный фолликул).
Основные причины боли во время овуляции
Часто женщины не понимают, по какой причине у них болит низ живота в середине цикла. Рассмотрим этот вопрос более подробно:
– боль возникает по причине слишком большого размера фолликула, который растягивает яичник;
– фолликул разрывается, и в брюшную полость попадает небольшое количество жидкости, что и вызывает раздражение брюшины;
– также при разрыве повреждаются кровеносные сосуды, и с жидкостью в брюшную полость попадает кровь. Это тоже действует раздражающе на стенки;
– в норме боль не длится более двух суток, поскольку кровь с жидкостью всасываются в слизистую;
– маточные трубы усиленно работают для успешного захвата яйцеклетки, этот процесс может доставлять женщине дискомфорт;
– в редких случаях боль вызывает наступившая беременность.
Если боль довольно сильная, не исключены спайки в брюшной полости. Они возникают после перенесенного воспалительного процесса, хирургического вмешательства, а также если у женщины имеется эндометриоз. Вот от чего болит живот в середине цикла. Овуляция пройдет, а вместе с этим утихнет боль.
Как помочь себе?
Прежде чем заниматься самолечением, необходимо обязательно убедиться в том, что боль вызвана разрывом фолликула, а не более серьезными и опасными заболеваниями. Для этого следует посетить гинеколога.
Именно врач должен дать рекомендации по уменьшению болей:
– в середине цикла женщине не стоит излишне нервничать;
– физические нагрузки следует уменьшить;
– соблюдать диету, то есть исключить слишком тяжелую пищу, а также продукты, которые приводят к сильному образованию газов в кишечнике;
– теплая ванна поможет облегчить боль, также допустимо использовать грелку на низ живота. Но это можно делать только в том случае, если нет воспалений;
– врачи часто рекомендуют принимать препараты из группы нестероидных противовоспалительных для снятия болевого синдрома и облегчения состояния во время овуляции. К наиболее подходящим можно отнести «Ибуклин», «Кетапрофен»;
– «Но-шпа», «Спазган» применяются для снятия спазмов.
Если боли при овуляции слишком мучительно, то гинекологом могут быть назначены оральные контрацептивы, чтобы исключить вызревание яйцеклетки.
Женщинам, которые хотят забеременеть, нельзя принимать никакие медикаменты, а также согревать грелкой низ живота. Это может негативно отразиться на качестве яйцеклетки.
Что делать при острой боли?
Если боль в середине цикла слишком сильная, это может быть какая-либо патология, например:
– внематочная беременность;
– воспаление придатков;
– апоплексия яичника;
– перекрут кисты;
– разрыв кисты;
– приступ аппендицита;
– гиперстимуляция яичников при приеме некоторых лекарств.
Сильную боль не нужно долго терпеть, нужно обязательно обратиться к врачу.
Когда очень сильно болит живот в середине цикла, в некоторых случаях помощь должна быть незамедлительной. Итак, нужно вызвать скорую, если:
– боль нестерпимая и продолжительная;
– происходит ухудшение состояние женщины;
– высокая температура тела;

– женщина теряет сознание;
– ситуация осложняется тошнотой и рвотой;
– открывается кровотечение;
– появление боли после приема медикаментов.
Заключение
Итак, может болеть живот в середине цикла. Не стоит пугаться, но лучше проконсультироваться с лечащим врачом, чтобы исключить серьезную патологию.
Содержание статьи:
Схваткообразные боли в животе, отдающие в поясницу, перед началом и в первые дни менструации знакомы каждой женщине и девушке. Их причиной является отслоение от стенок матки эндометрия – необходимого для развития эмбриона рыхлого эпителиального слоя, пронизанного кровеносными сосудами. Если зачатия не происходит, организм избавляется от ненужной ткани. При этом низ живота начинает тянуть, сократительная деятельность маточной мускулатуры вызывает спазмы, сопровождающиеся кровянистыми выделениями – начинаются месячные, знаменующие собой старт очередного менструального цикла. Но иногда женщины ощущают болезненность, напоминающую предменструальную, за полторы-две недели до его начала.
Физиологические причины болей
 Тянущие боли внизу живота, как перед месячными, в середине цикла у женщин могут иметь несколько причин как физиологического, так и патологического происхождения. В первом случае их вызывают специфические особенности женского организма, имеющие отношение к его репродуктивной функции. Чаще всего физиологическая боль в этот период объясняется овуляцией – так называется процесс отделения созревшей яйцеклетки от яичника. Иногда она бывает настолько крупной, что разрывает стенки фолликула, повреждая кровеносные сосуды. Поэтому возможно выделение небольшого количества крови. Боль может локализоваться как справа, так и слева. Как правило, при каждой овуляции происходит отделение от правого либо левого яичника только одной яйцеклетки.
Тянущие боли внизу живота, как перед месячными, в середине цикла у женщин могут иметь несколько причин как физиологического, так и патологического происхождения. В первом случае их вызывают специфические особенности женского организма, имеющие отношение к его репродуктивной функции. Чаще всего физиологическая боль в этот период объясняется овуляцией – так называется процесс отделения созревшей яйцеклетки от яичника. Иногда она бывает настолько крупной, что разрывает стенки фолликула, повреждая кровеносные сосуды. Поэтому возможно выделение небольшого количества крови. Боль может локализоваться как справа, так и слева. Как правило, при каждой овуляции происходит отделение от правого либо левого яичника только одной яйцеклетки.
Боль в животе в середине цикла при овуляции напоминает признаки дисменореи. Интенсивность болевой симптоматики, вызываемой овуляторным синдромом, обычно намного слабее – это скорее покалывание, которое продолжается не более суток. Из всех трех фаз, входящих в менструальный цикл – фолликулярной, овуляционной и лютеиновой – средняя самая короткая: продолжительность процесса овуляции не превышает 32 часов.
Еще одна физиологическая причина того, что у женщины в середине цикла болит низ живота, как при месячных, – беременность. Период овуляции наиболее благоприятен для зачатия, и если оно происходит, эмбрион, продвигаясь по фаллопиевым трубам, попадает в матку. Там он старается имплантироваться для дальнейшего развития, вживляясь в эндометриальный слой и повреждая при этом его ткани. Процесс сопровождается выделением белой или розоватой слизи. Также при этом может ощущаться чувство некоторого напряжения в грудных железах.
Если болевой синдром, возникающий в середине менструального цикла, носит кратковременный характер и не становится таким сильным, как во время месячных, он не должен пугать женщину. Ситуация нормализуется естественным образом без медицинского вмешательства, как только овуляция, либо вживление зародыша в матку завершится.
Чтобы облегчить состояние, рекомендуется некоторое время спокойно полежать на боку, приняв «внутриутробную» позу: голова слегка наклонена вперед, ноги максимально согнуты в коленях и прижаты к животу. Можно приложить теплую (не горячую!) грелку.
Патологические причины болей
 Боль, спазмы и чувство тяжести внизу живота у женщин в середине менструального цикла могут иметь и патологическую этиологию. Такую симптоматику в первую очередь способны вызывать заболевания органов женской репродуктивной системы. К ним относится эндометрит – воспаление слизистой оболочки внутриматочной полости, эндометриоз – патологическое разрастание эндометрия, воспаление яичников и маточных труб (аднексит), разрыв кисты яичника, перекручивание кистозной ножки, внутриматочные спайки, фибромы и миомы. Помимо болезненных ощущений они могут сопровождаться выделениями коричневого цвета, иногда с неприятным запахом, и даже кровотечением.
Боль, спазмы и чувство тяжести внизу живота у женщин в середине менструального цикла могут иметь и патологическую этиологию. Такую симптоматику в первую очередь способны вызывать заболевания органов женской репродуктивной системы. К ним относится эндометрит – воспаление слизистой оболочки внутриматочной полости, эндометриоз – патологическое разрастание эндометрия, воспаление яичников и маточных труб (аднексит), разрыв кисты яичника, перекручивание кистозной ножки, внутриматочные спайки, фибромы и миомы. Помимо болезненных ощущений они могут сопровождаться выделениями коричневого цвета, иногда с неприятным запахом, и даже кровотечением.
К негинекологическим причинам гипогастрального болевого синдрома относятся:
- Заболевания, передающиеся половым путем, такие как хламидиоз или гонорея.
- Острый или хронический цистит – воспаление мочевого пузыря, характеризующееся частым мочеиспусканием и жжением в области мочеточника.
- Проктит – воспалительный процесс слизистой оболочки прямой кишки.
- Геморрой – воспаление геморроидальных узлов, расположенных вблизи анального отверстия.
- Трещины в заднем проходе – в этом случае боль обостряется в момент дефекации.
- Непроходимость кишечника – ее может спровоцировать как новообразование в брюшной полости, так и скопление каловых масс, вызванное запором.
- Воспаление почек – пиелонефрит. При этом заболевании повышается температура тела, появляются рези при мочеиспускании, ноет поясница.
- Почечная колика – для данной патологии характерно острое проявление абдоминального болевого синдрома, порой доводящее пациента до шокового состояния.
- Приступ почечнокаменной или мочекаменной болезни наряду с болью вызывает затруднение оттока мочи, которая приобретает мутно-красноватый оттенок.
- Аппендицит – иррадиация боли зависит от расположения червеобразного отростка слепой кишки, который не имеет четкой локализации в брюшной полости. Аппендикс может находиться как неподалеку от желудка, так и доходить до области малого таза, тогда его воспаление вызывает боль внизу живота.
При возникновении тревожных симптомов следует как можно скорее обратиться к врачу или вызвать бригаду скорой помощи. Разрыв яичниковой кисты, приступ аппендицита, почечнокаменной либо мочекаменной болезни, а также кишечная непроходимость требуют неотложной госпитализации с целью проведения хирургического вмешательства.
Диагностические процедуры
 Первый врач, к которому женщина должна обратиться с жалобой на боль внизу живота – это терапевт. После первичного осмотра, заключающегося в пальпации брюшины, он направляет пациентку к гинекологу либо хирургу, иногда к обоим специалистам одновременно. Кроме того, назначается проведение лабораторных исследований крови и мочи на предмет выявления признаков воспалительного процесса в организме.
Первый врач, к которому женщина должна обратиться с жалобой на боль внизу живота – это терапевт. После первичного осмотра, заключающегося в пальпации брюшины, он направляет пациентку к гинекологу либо хирургу, иногда к обоим специалистам одновременно. Кроме того, назначается проведение лабораторных исследований крови и мочи на предмет выявления признаков воспалительного процесса в организме.
Гинекологические виды обследования включают:
- Колькоскопию – исследование шейки матки на предмет обнаружения патологических изменений ткани. После нанесения на слизистую оболочку специального состава здоровые клетки меняют цвет, а больные остаются прежними. Изменения обнаруживаются при осмотре с помощью зеркала, вводимого во влагалище.
- Гистероскопию – малоинвазивную методику исследования внутриматочной полости при помощи специального аппарата – гистероскопа. Поскольку для его введения требуется максимально расширить цервикальный канал – шейку матки, манипуляция проводится под общим наркозом. Методика позволяет совмещать обследование с малоинвазивным хирургическим вмешательством – удалением полипов, остатков плодного яйца либо внутриматочного контрацептива (спирали). С помощью гистероскопа берутся пробы ткани для дальнейшего исследования.
При подозрении на инфекции, передающиеся половым путем, делается соскоб слизистой оболочки для проведения бактериального посева. Таким образом выявляется хламидиоз и гонорея.
Также проводится ультразвуковое исследование органов малого таза, позволяющее обнаружить функциональные и структурные нарушения в органах мочевыделительной и половой систем. УЗИ у женщин проводится двумя способами: абдоминальным – через переднюю стенку брюшного пресса (определяются патологии почек и мочевого пузыря, либо воспаление аппендикса), и трансвагинальным – через влагалищный вход (при подозрении на гинекологические заболевания). Для уточнения результатов УЗИ органов малого таза дополняется компьютерной и магнитно-резонансной томографией.
Терапия и профилактика
Терапия патологического болевого синдрома внизу живота зависит от его этиологии и характера. При эндометриозе, а также на ранних стадиях фиброматоза в курс лечения входят гормональные средства. Воспалительные процессы гасятся антибиотическими либо антибактериальными препаратами, принимаемыми по назначению и под контролем врача.
Боль в животе в середине цикла
По каким причинам возникает боль в животе в середине цикла?
Такая боль очень часто возникает из-за кровотечения из яичника, правда, это кровотечение небольшое. Возникает оно в основном в середине цикла. Это кровотечение часто раздражает стенку брюшной полости, из-за чего она воспаляется и болит. Позже кровотечение уже не беспокоит, кровь сворачивается. Но боль во время кровотечения может быть как сильной, так и слабой. Это зависит от особенностей организма женщины и характера кровотечения – какой он – сильный или слабый.
Одной из причин боли в животе в середине цикла может быть расстояние между брюшной стенкой и яичником. Если оно невелико, то боль может быть более интенсивной. А боль в середине цикла, как правило, вызвана овуляцией – выходом яйцеклетки из яичника. Овуляция хоть и вызывает сильную боль внизу живота, но не провоцирует других заболеваний мочеполовой системы. Это положительный момент. Хорошо также то, что эти боли не провоцируют дополнительных заболеваний репродуктивной системы.
Боли внизу живота или в середине живота во время цикла могут быть следствием многих заболеваний репродуктивной системы. Эти заболевания – киста яичника, воспаление придатков, миома матки, инфекции мочеполовой системы. Если такие боли проявляются, лучше всего сразу же обратиться к врачу для выяснения причин. Если мочеполовая система здорова, значит, это могут быть заболевания органов малого таза. Причинами также могут быть растяжения мышц, а также связок, соединяющих внутренние органы.
Эмоции, вызванные стрессом, могут повредить здоровью внутренних органов женщины. Но как стресс может повлиять на здоровье печени или почек? Очень просто. Органы крепятся к позвоночному столбу с помощью связок. Когда женщина нервничает или испытала шок, связки спазмируются и органы могут менять положение. Таким образом. Нервные окончания и сосуды, которые пронизывают органы, тоже могут перекручиваться, а от этого возникают сильные боли. Если это совпадает с серединой цикла, боли могут усиливаться. Спазмы, которые возникают из-за сокращения мышц, обязательно нужно лечить, чтобы нейтрализовать боли. Врач проконсультирует и поможет справиться с этим состоянием.
Боли в животе в середине цикла по причине гинекологических проблем
Одна из самых популярных причин, по которой у женщины в середине цикла развиваются боли, это воспаления органов репродуктивной системы. Если разрушительные процессы внутри живота в середине цикла приняли острый характер, боль может локализоваться в одном участке. При этом женщина может болеть, у нее может сильно повыситься температура тела.
Боли у женщины внутри живота во время цикла могут быть тянущими и усиливаться или возникать после осмотра у гинеколога, а также после осмотра ректальной области. Это довольно опасно, поскольку органы малого таза воспаляются, и это требует скорейшей помощи врача. Это также сильно влияет на репродуктивную способность женщины.
 [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]
[4], [5], [6], [7], [8]
Почему возникают боли во время овуляции?
Боли во время овуляции могут возникать из-за того, что выходящий из яичника фолликул развивает его тонкую оболочку. Это может вызывать боли, довольно сильные. Эти боли дислоцируются в районе малого таза и носят опоясывающий характер. Длится такая боль от 3-4 часов до 2-3 суток. Это довольно долго. Поэтому такие боли требуют дополнительной консультации врача. Тем более если боли сопровождаются вялостью и повышенной утомляемостью. В таком случае можно принять таблетку но-шпы – она снимет спазмы и обезболит.
Если боли внизу живота сопровождаются еще и выделениями крови из влагалища, стоит обеспокоиться. Тогда нужно немедленно обратиться к гинекологу за консультацией. Причинами болей могут быть такие заболевания как киста в районе цервикального канала, эндометрит или миометрит.
Другие причины боли в животе в середине цикла
Боль в животе в середине цикла – серьезная проблема, которая может возникать при наличии тяжелых заболеваний. Поэтому, если эта боль длится более двух часов, лучше обратиться к врачу для консультации.
 [9], [10]
[9], [10]

Незначительная тянущая боль внизу живота знакома многим женщинам. Но не все знают, почему она возникает и является ли это нормой. Особое беспокойство вызывает необычно сильная боль или появление болезненных ощущений при условии, что раньше их никогда не было. Почему может болеть матка или яичник?
На самом деле очень сложно сказать, что стало причиной боли в середине цикла. Это может быть нормой или свидетельствовать о серьёзных проблемах со здоровьем, когда нужно срочно обращаться за медицинской помощью. Точно сказать, что вызвало дискомфорт, сможет лишь врач, но женщине тоже важно знать возможные причины.
Гинекологические

Тянущие боли внизу живота очень часто оказываются связанными со здоровьем половой сферы. Если женщина замечает четкую связь с периодами менструального цикла и временем появления неприятных ощущений, для решения проблемы в первую очередь ей необходимо проконсультироваться с гинекологом.
Также стоит обратить внимание на наличие или отсутствие другой симптоматики. Например, могут появляться выделения, может тошнить, а при некоторых состояниях возможен даже обморок. Для того чтобы понять, как избавится от дискомфорта, не навредив себе, важно быть очень внимательной и разобраться, что именно происходит.
Физиологические
Если болит живот в середине цикла, это не обязательно является признаком какой-то болезни. Особенно верно это в тех случаях, когда неприятные ощущения очень слабые и регулярно повторяются в определенных ситуациях. Обычно в таких случаях женщины сами знают или догадываются, что с ними происходит.
Возможные естественные причины, почему тянет низ живота в середине цикла:
- Овуляция. Обычно бывает за 12–14 дней до ожидаемой даты следующей менструации. В этот день зрелая яйцеклетка выходит из яичника, что сопровождается микроскопическим кровотечением. Кровь может попадать на брюшную стенку и раздражать её, вызывая небольшое воспаление. Это может чувствоваться, особенно если у девушки низкий болевой порог. Дискомфорт не длится дольше 2 дней, обычно только несколько часов. Чаще всего, кажется, что болит яичник, но может быть похоже на боль при месячных.
- Беременность. На ранних сроках беременности матка еще не достигла таких размеров, чтобы её могли поддерживать кости таза, и нагрузка идёт на связки. Этот фактор и факт увеличения матки может приводить к сдавливанию близлежащих рецепторов, что вызывает ноющие боли в пояснице. Но это происходит постепенно и не настолько выражено, чтобы мешать жить привычным образом.
- Возрастные особенности. В подростковом возрасте цикл бывает нестабильным. Месячные могут начинаться раньше или позже на пару недель, может меняться продолжительность цикла. В таком случае болезненность может быть связана с приближением менструации, в то время как девушка думает, что до них ещё далеко. Кроме того, в разных циклах чувствительность к гормональным перепадам может быть разной, поэтому нет ничего удивительного, если в каком-то месяце овуляция будет чувствоваться сильно, хоть раньше не ощущалась.
Обычно такие неприятные ощущения внизу живота или в области поясницы проходят или заметно уменьшаются в состоянии покоя. Для этого нужно удобно лечь, укрыться, приложить тепло, желательно пить достаточно тёплой жидкости. Поэтому, если боль тянущая и не мешает нормально жить и работать, женщина знает, что у неё в этот период должна быть овуляция или она могла забеременеть, ни в коем случае не стоит сильно волноваться. Иногда достаточно подождать несколько часов, чтобы всё прошло. Если беспокойства остаётся, можно сходить к врачу.
Патологические
Если боли внизу живота в середине цикла появились впервые или очень сильно выражены, скорее всего, это говорит о развитии в организме какого-то патологического процесса. Если дискомфорт не сильный, но постоянный, стоит, не откладывая на потом, сходить в больницу. Если кроме болезненных ощущений, присутствует слабость, бледность, тошнота, кровотечение или потеря сознания, необходимо сразу же вызвать врача на дом.
Существует огромное количество патологических состояний, которые могут проявляться болевыми ощущениями внизу живота. При этом их выраженность может варьироваться от тянущих или ноющих, которые только немного мешают, до острых, способных вызвать болевой шок.
Вот некоторые из них:
- Инфекция. При этом могут наблюдаться выделения, возможно с неприятным запахом. В области наружных половых органов возникает зуд или жжение. Но при переходе в хроническую форму болезни могут присутствовать лишь ноющие боли внизу живота. Этот фактор нельзя исключать, если был незащищенный секс, но после него еще не сдавался анализ на инфекции.
- Переохлаждение. Если на днях замерзли ноги, живот или спина, есть большие риски простудить яичники.
- Хронические заболевания репродуктивной системы.
- Новообразования: кисты, полипы, онкология. Боль обычно сочетается с небольшим выделением кровянистых или коричневатых выделений.
- Внематочная беременность, разрыв трубы. Обычно боль локализируется с одной стороны, где находится пораженная труба. Состояние быстро ухудшается, поднимается температура.
- Выкидыш или замершая беременность. Характерен схваткообразный характер боли, кровянистые выделения.
- Гормональный сбой. Обычно этот диагноз ставят, если самочувствие женщины заметно отличается от обычного в этот период менструального цикла, но нет никаких видимых факторов, которые могли бы этому способствовать. Подтверждается анализами. Может быть вызвано любым сильным стрессом.
- Разрыв кисты яичника или самого яичника. Боль резкая, вплоть до шока.
- Спайки. Болезненность чувствуется не только в середине цикла, но и некоторых других ситуациях, например, при резких движениях или во время секса. Острая боль появляется при разрыве спайки.
В любом из перечисленных выше состояний необходимо лечение, иногда экстренное (при внематочной беременности, выкидыше, разрыве кисты). Но в любом случае начать нужно как можно быстрей. Но лекарства не следует подбирать самостоятельно, чтобы не усугубить положение. Если неизвестны причины плохого самочувствия, нежелательно прикладывать грелку ил другое тепло, так как это может усилить кровотечение.
Негинекологические

Конечно же, живот может болеть и по другим причинам, которые совсем не связаны с половой сферой. Это могут быть любые болезни внутренних органов, особенно острые состояния. В таких ситуациях болезненность обычно возникает без связи с периодом менструального цикла.
Возможные варианты:
- Аппендицит.
- Воспаление почек. Характерный признак этого состояния – изменение внешнего вида мочи (помутнение, красноватый оттенок, наличие хлопьев). Часто болит не только низ живота, но и поясница.
- Почечная колика. Ощущение способны вызвать болевой шок, обычно локализуются с одной стороны.
- Проблемы с кишечником. Живот может ныть из-за запора, резкая боль возникает при непроходимости.
- Цистит. Чувствуется резь и жжение, которое усиливается при мочеиспускании.
Можно сделать вывод, что если из месяца в месяц в середине цикла тянет низ живота, это может быть просто признаком наличия овуляции. Поэтому не стоит чрезмерно переживать. Но не будет лишним сходить к врачу и убедиться, что всё в порядке. Каждой женщине необходимо раз в полгода посещать гинеколога. Но если боль резкая, длительная, сопровождается необычными симптомами, визит в больницу откладывать нель
Почему болит низ живота в середине цикла
Боли внизу живота в середине цикла могут проявиться по самым разным причинам и даже не обязательно гинекологическим, поэтому игнорировать и терпеть их категорически нельзя, в особенности если вам самим непонятно, почему они вас беспокоят. Для любой женщины халатное отношение к себе может стать просто губительным, особенно если она еще собирается рожать детей.
В зависимости от заболевания, боли в животе в середине цикла могут проявляться с одной стороны или распространиться по всему животу, отдавать в поясницу, быть резкими, острыми, тянущими, ноющими, сильными или нет. Характер их дает возможность постановки диагноза и определения правильного лечения, с которым затягивать категорически запрещено.
Овуляция
Большинство женщин могут наблюдать у себя несильные боли в низу живота в середине цикла, которые доставляют дискомфорт. Данное состояние обуславливается тем, что фолликулярной жидкостью немного раздражается брюшина. Практически всем женщинам об этом, конечно же, известно, и потому они не идут за помощью к врачам, так как данный факт является нормой и не требует никакого вмешательства. Но все это справедливо, только если боли являются не слишком сильными.
Заболевания яичников
В зависимости от того, какой яичник поражен, боли в низу живота в середине цикла проявляются приступами, локализованными с одной стороны. Причиной может быть разрыв, воспаление или апоплексия яичника. Кроме того, не стоит списывать со счетов и злокачественные или доброкачественные новообразования. В данном случае раздражается брюшина за счет появления крови или ишемии, а также появляются очень сильные боли, которые могут носить постоянный характер.
Заболевания половых органов
По причине попадания в матку или влагалище патогенных микроорганизмов начинает развиваться воспаление, которое проявляется возникновением боли в животе в середине цикла, неприятными ощущениями, выделениями и другими признаками. Также при воспалительных процессах происходит образование спаек, которые приводят к возникновению сильнейшего дискомфорта. А при их разрывах возникает острая и очень сильная боль, которая может даже вызывать шоковое состояние.
Аппендицит
Основными симптомами данного заболевания являются нечеткие коликообразные боли и выделения в середине цикла, которые со временем становятся только сильнее. Сначала боль может появиться с правой стороны, а затем переместиться в верхнюю часть живота. Изначальн
90000 Why does lower abdomen hurt men and women and what to do? | Competently about health on iLive 90001 90002 If the lower abdomen hurts? 90003 90004 Regardless of who suffers from pain, man or woman, there are common signs of emergency conditions and rules of conduct in such cases. 90005 90004 It hurts lower abdomen, what needs to be done and what can not be done in any case. 90005 90004 A condition that in clinical practice is characterized as “acute abdomen” is a serious threat not only to health, but also to life, accompanied by the following symptoms and signs: 90005 90010 90011 Acute, intolerable pain that lasts for an hour.90012 90011 Significant increase in pain at the slightest tension or cough, when turning over or any movement. 90012 90011 Pain in the lower abdomen, which does not change its intensity with a change in posture or position of the patient. 90012 90011 If before the appearance of pain during the day there was no bowel movement, the abdomen is tense and swollen, this may indicate an acute intestinal obstruction. 90012 90011 The stomach does not just hurt much, it is tense. 90012 90011 Lower abdominal pain is accompanied by increased heart rate, sweating, pale skin, a decrease in blood pressure and even fainting, loss of consciousness.90012 90011 If the pain is accompanied by a bowel movement, in which there are blood clots in the feces (black or uncharacteristic feces). 90012 90025 90004 In any case, it is almost impossible to independently diagnose and differentiate a serious, threatening disease from others that do not require emergency care. Therefore, with severe pain, persistent for an hour, fever, weak pulse, nausea and vomiting, you need to call an ambulance. 90005 90004 Before the arrival of specialists, the following independent actions are allowed: 90005 90010 90011 The patient needs – complete rest, silence, ventilated room and horizontal position.90012 90011 You can put a cold water heater with ice, a cooled water bottle, a cold compress on the abdominal area. The cold can not be kept more than 20-25 minutes, cold compresses should be changed in order to avoid warming the abdomen. 90012 90011 Of the medicaments, let us accept a No-shpy, no more than two tablets. All other drugs can be prescribed only by a doctor after an examination and a preliminary diagnosis. 90012 90011 If there are signs of internal bleeding – fainting, bluish complexion, increased heart rate, and there is a health worker next to it, you can put an intravenous drip of sodium chloride solution.90012 90025 90004 It hurts lower abdomen, the following actions are unacceptable: 90005 90010 90011 You can not choose and take painkillers yourself. At a minimum, this “lubricates” the clinical picture and makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis, as a maximum – it provokes an even greater exacerbation of the underlying disease. 90012 90011 You can not warm the stomach in order to avoid the development of extensive sepsis, let’s say only cold. 90012 90011 You can not take medications from a number of laxatives, enemas are unacceptable.90012 90011 You can not take food or drink. With a strong dry mouth, it is acceptable to wet the tongue and lips. 90012 90025 90004 This is a recommendation that applies to both men and women, especially you need to be attentive to the painful symptoms in children who still do not know how to properly describe their feelings. At the slightest warning signs of malaise in a child, you should immediately seek medical help. 90005 90004 90055 [3], [4] 90005 90002 It hurts lower abdomen during menstruation 90003 90004 Such pain is most common in young women, whose hormonal system has not yet stabilized.Menstruation itself is not a disease, it is a natural physiological condition that ensures the fertility of a woman. If all the organs and systems of a woman work flawlessly, then the menstrual cycle should not cause discomfort. Some pain may occur in the first two or three days of the cycle, and then pass. The lower abdomen hurts during menstruation, usually because of dissonance between different types of sex hormones – prostaglandins and progesterone. The uterus produces substances that provide its contractile function – prostaglandins.If there are too many of them, the contractions become intense, the pain increases accordingly. Also, an excess of prostaglandins can provoke headaches, nausea and even vomiting. Elevated levels of contractile hormones are characteristic of young women who have not yet given birth. If the lower abdomen hurts during menstruation in women who have given birth, this may be evidence of more serious pathologies – endometriosis, uterine fibroids, adnexitis, inflammation in the ovaries, in the fallopian tubes and many other diseases.In addition, poorly selected intrauterine device can also provoke painful sensations during menstruation. Abdominal pain may be accompanied by other signs, among which the most common are: 90005 90010 90011 Pain radiating to the lumbar region. 90012 90011 Heaviness and pain in the legs. 90012 90011 Nausea, vomiting. 90012 90011 Impaired bowel movements, diarrhea or constipation. 90012 90011 General weakness. 90012 90011 Irritability, tearfulness, often increased aggressiveness.90012 90025 90004 Emergency medical care is necessary for pain during menstruation, if the following symptoms appear: 90005 90010 90011 The pain becomes intense with increased bleeding. The dough is a sanitary pad that overflows in one hour. 90012 90011 In addition to pain, the woman feels fever, fever, sweating. 90012 90011 The pain is accompanied by severe aching in the joints. 90012 90011 Abdominal pain accompanied by dizziness and loss of consciousness. 90012 90025 90004 90055 [5], [6], [7] 90005 90002 After monthly pain in lower abdomen 90003 90004 This is typical for conditions caused by excessive levels of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the contractile function of the uterus.During the cycle, the uterus must contract to remove blood clots; after the cycle ends, the contractions become less active. However, if a woman’s hormonal system works with disorders, there is an imbalance of hormones in it, there may be pain even after the menstrual cycle. Often in women 30-35 years old there is an increase in estrogen production, which leads to lower abdominal pain during the cycle, which can also change and stray. As a compensatory response, the uterus begins to intensively produce prostaglandins, which continue to contract the organ even after the end of menstruation.Postmenstrual pain in the lower abdomen is often caused by stress or depression. As a result, a hard flowing cycle disrupts the functioning of the thyroid gland, which controls hormonal balance. It turns out a kind of vicious circle in which one pathological factor provokes another. In addition, after menstruation, lower abdomen often hurts because of a congenital anomaly of the uterus – underdevelopment or its wrong position. Any inflammatory process – adnexitis, salpingitis can cause long postmenstrual pain.The intrauterine device, irritating walls, uterus cavity can also interfere with normal uterine contraction. In situations where the pain after the cycle does not stop for two or three days, do not worry, it is most likely the usual physiological hormonal “jump”. If, after menstruation, the lower abdomen hurts for four or more days, especially if there is a discharge and increased body temperature, you should consult a doctor to rule out a serious inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. 90005 90004 90055 [8] 90005 90002 After ovulation lower abdomen hurts 90003 90004 It is also a common phenomenon in gynecological practice, women often complain of lower abdominal pain during the period of follicle maturation and uterine contraction.Surprisingly, even women who gave birth sometimes do not know what ovulation is and how the fertilization process is associated with it. 90005 90004 Ovulation is the period in which a ripe follicle “releases” into the abdominal cavity a single egg cell ready for fertilization. This process begins with the first menstrual cycle and gradually fades out during menopause. If a couple plans to replenish the family, then ovulation days are the most favorable days for conceiving a baby. The period of ovulation for each woman is different and depends on the length of the monthly cycle.The boundaries of the ovulation period range from 22 to 33-35 days. Ovulation is often accompanied by painful symptoms, in addition, during this period, fertility (attraction) to the opposite sex increases significantly, which is proof of the natural predisposition of these days to conceive. Pain, both during ovulation and after it, is most often of moderate intensity and is an acceptable physiological norm. Rarely, the pain becomes severe, cramping, but, as a rule, it does not last long. If the pain is interspersed from the left side to the right side, this indicates maturation of the follicle in the left and right ovary.Pain after ovulation is very rare, and if they occur, it may indicate the following conditions: 90005 90010 90011 Exacerbation of chronic, latent inflammation in the ovaries. 90012 90011 The accomplishment of conception. 90012 90011 Pregnancy, which may be associated with some inflammatory processes in the ovaries. 90012 90011 Pathological processes in the pelvic organs, not associated with the maturation of the follicles and the release of the egg. 90012 90025 90004 90055 [9], [10], [11] 90005 90002 Sore lower abdomen and discharge 90003 90004 This is a sign of the inflammatory process, which goes into an exacerbation stage.Often, pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by secretions of a milky color, is a symptom of a common disease – thrush or candidiasis. In fact, it is also an inflammation of the vagina, but it is usually caused by Candida albicans – specific yeast-like organisms, fungi. The reasons for which the lower abdomen hurts and the discharge becomes abundant, characteristic of its curd consistency, are very diverse. Among the most common are the following: 90005 90010 90011 Endocrine system pathology – hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism.90012 90011 Diabetes mellitus, in which high blood sugar levels, respectively, and vaginal secretions. The acidity of the secretion is reduced, which creates a favorable, comfortable environment for the reproduction of Candida albicans. 90012 90011 Metabolic disorders, obesity or anorexia. 90012 90011 Long-term use of medicines – antibiotics, hormonal drugs. 90012 90011 Physiological changes in the body – menopause. 90012 90011 Long-term use of contraceptive drugs. 90012 90011 Diseases of venereal etiology.90012 90011 Infectious diseases of the pelvic organs – mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis. 90012 90011 The consequence of surgical intervention in which the body undergoes the process of adaptation. 90012 90011 The change of the climatic zone, especially often provokes pain in the lower abdomen and the release of moving to hot countries. 90012 90011 A general decrease in the protective functions of the immune system. 90012 90011 Avitaminosis. 90012 90025 90004 Thrush is not a threat to the health of the disease, but its chronic course can provoke an erosive process in the cervix, which is considered to be quite a serious pathology.90005 90004 It is also a sign of the inflammatory process in the appendages. Inflammation of the appendages can be manifested by painful sensations on the left or on the right side, radiating to the thigh or sacral region of the loins. Excretions in inflammation mucous, often with pus. The body temperature may rise, a feverish state occurs, which indicates an exacerbation of the process. 90005 90004 Also, abdominal pain can be regular, but not pronounced, the allocation of scarce, but these symptoms also can not be ignored, to prevent exacerbations and more serious problems that may require emergency surgical care.90005 90004 90055 [12], [13], [14] 90005 90002 Sore lower belly after sex 90003 90004 This is evidence of pathological processes that may be hidden in the body, but often such pains are provoked by psychogenic factors. 90005 90004 The lower abdomen after sex hurts – it is also a symptom of standard gynecological problems requiring diagnostics and treatment. Pain in the lower abdomen after sexual contact may indicate ruptures of an ovarian cyst, ruptures of the ovary itself, or the threat of miscarriage in the early stages of childbearing.In addition, the cause of the pain can be purely mechanical, when sexual contact was too rough, intense and provoked injury to the vaginal wall, damaged the mucous membrane of the cervix. If the lower abdomen hurts after sex and discharge with blood, urgently seek medical help, especially if the bleeding is intense. 90005 90004 90055 [15], [16], [17] 90005 90002 Week hurts lower abdomen 90003 90004 This constant abdominal pain is called chronic abdominal pain. Descriptions of sensations on the part of patients are very diverse – from a burning sensation to constant pressure and severity.Quite often, the reason that a lower abdomen hurts for a whole week is an elementary eating disorder, the gastrointestinal tract is simply unable to work rhythmically in normal mode. However, often chronic, persistent pain in the lower abdomen may indicate a developing gallstone disease, pancreatitis, an inflammatory process in the large intestine. The pain can be really constant, but it can also be cramping. As a rule, if a person suffers pain in the lower abdomen for a week, the pain is rather weak and does not differ in intensity.It is important to note how pain is associated with food intake, whether it occurs before or after meals. Also, chronic abdominal pain may be a symptom of a psychosomatic illness, more associated with neurology than with gastroenterology. In clinical practice, these pains are called neurotic. 90005 90004 The stomach actually hurts, although there are no objective external or internal causes. This is due to the psycho-emotional factor, which may be unloved work, intense study and fear of exams, family troubles.Also the cause of persistent pain can be vegetative-vascular syndrome, which is also a neurological disease. One of the causes of chronic, recurrent pain is helminthic invasion. Chronic pains are diagnosed through a comprehensive examination, the more complete it is, the more accurate and effective the treatment will be. The standard diagnostic complex includes the following procedures: 90005 90010 90011 Collection of anamnestic information, including family information. 90012 90011 Palpation of the abdominal area.90012 90011 Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy – FGDs. 90012 90011 A comprehensive clinical study of blood, including leukocyte formula. 90012 90011 Biochemical blood test, which determines the level of enzymatic activity of the liver, pancreas. 90012 90011 Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. 90012 90011 Analysis for the determination of helminthic invasion, coprogram. 90012 90025 90002 If lower abdomen hurts 90003 90004 However, there are conditions that require immediate medical care, it is all strong pain, persistent for an hour.90005 90004 Severe pain in the lower abdomen is one of the most typical symptoms shown in gastroenterological and gynecological practice. The stomach hurts most often intensively, since there are thousands of nerve endings and pain receptors in the gastrointestinal tract. The nature of the pain can be different: pulling, sharp, aching, cutting and so on. The pain symptom in the abdominal area is not specific, since many diseases are accompanied by painful sensations. 90005 90004 Women have lower abdominal pain during the menstrual cycle; in men, lower abdominal pain can be a sign of urological pathology.90005 90004 One of the main reasons that cause severe pain in women in the absence of signs of pregnancy are the following: 90005 90010 90011 Ectopic pregnancy, in which the egg does not reach the uterus and begins to implant in the fallopian tube. Signs of pregnancy may be absent, but after three to four weeks, the egg begins to grow and destroy the tissue of the fallopian tube. This process is accompanied by severe pain, nausea, dizziness before losing consciousness. Such a condition requires immediate surgical intervention.90012 90011 Apoplexy, ovarian rupture. The rupture can be caused by injury, intense physical exertion or sexual contact. Symptoms are very similar to signs of ectopic, tubal pregnancy. The pain may radiate to the lumbar region, accompanied by vomiting, weakness and loss of consciousness. The treatment is urgent, surgical. 90012 90011 Torsion and violation of the outflow of blood through the veins in the leg of an ovarian cyst. The cyst begins to grow rapidly, puts pressure on nearby organs, often merging with them.Abdominal pain is aching, quite strong, but transient and recurrent. Surgical treatment. 90012 90011 Inflammation of the appendages, which happens quite often after an abortive abortion, after childbirth. The pain is diffuse, strong, intermittent. If you do not make a timely diagnosis, the spread of infection can lead to peritonitis. In the acute stage, adnexitis produces severe pain in the lower abdomen with irradiation to the groin. The temperature is elevated, the abdominal muscles are very tense.Treatment in the initial stage of development of adnexitis medical, conservative, in the acute stage with the threat of peritonitis, surgical intervention is possible. 90012 90025 90004 In addition, the lower abdomen hurts when ureaplasmosis, pathological diseases of the urinary system. In men, acute pain in the lower abdomen is a typical sign of inflammation of the urethra, the acute stage of prostatitis, hernia incarceration. 90005 90004 All conditions associated with severe pain require immediate medical attention.90005 90004 90055 [18] 90005 90002 Sore back and lower abdomen 90003 90004 This is a description of the so-called pelvic pains. Pelvic pain is considered all the pain in the lower abdominal part, accompanied by pain in the sacrum, lumbar region. Often such pains in men give (irradiate) to the rectum or vagina in women. The lower back and lower abdomen hurts – it is a nonspecific symptom that may indicate various diseases, both gynecological, proctological, and vascular or urological. By the nature of the pain is also different, they can be acute or chronic, prolonged.90005 90004 Acute back pain is a sudden pain that lasts two to three hours, combined with fever, nausea, weakness and fever. So often acute conditions that require immediate surgical care manifest themselves – appendix inflammation, intestinal acute obstruction, an attack of cholecystitis, rupture of an ovarian cyst, purulent inflammation of the urethra, pyelonephritis and other diseases. 90005 90004 Chronic, prolonged pelvic pain is a recurring discomfort, sometimes lasting for months. Such pains indicate a developing latent pathology that does not yet manifest itself.90005 90004 90055 [19], [20] 90005 90224 Sore back and lower abdomen – causes and types of diseases 90225 90004 Gynecological causes: 90005 90010 90011 Endometriosis, which can take various forms: 90012 90011 Imbalance of the hormonal system, the disruption of the normal anatomical structure of the uterus, compaction of the walls and tissue deformation. 90012 90011 Vulvodynia (vaginal pain) caused by endometriosis. 90012 90011 Inflammatory process in the pelvic organs caused by endometriosis.90012 90011 Neoplasms (uterus, ovaries) – benign and malignant. 90012 90011 The omission of the walls of the vagina and uterus or the vet (prolapse of the pelvic organs). 90012 90025 90004 Urological causes: 90005 90010 90011 Interstitial cystitis is a disease of unknown etiology when bacterial studies do not identify the pathogen of the inflammatory process. 90012 90011 Infectious inflammation of the urinary tract. 90012 90011 Urolithiasis or urolithiasis. 90012 90011 Bladder cancer.90012 90011 Adhesive causes that often accompany surgery, as well as adhesive disease can develop and cause back pain as a result of a closed injury. 90012 90025 90004 Proctological causes: 90005 90010 90011 Hemorrhoids, which is manifested by chronic pelvic pain. 90012 90011 Inflammation of the mucous tissue of the rectum – proctitis. 90012 90011 Intestinal tumor. 90012 90025 90004 Neurological causes: 90005 90010 90011 IBS – irritable bowel syndrome. 90012 90011 Radiculopathy – inflammation of the spinal cord of the spinal cord or its infringement (sciatica).90012 90011 Hernia, osteochondrosis or prolapse (prolapse) of the intervertebral disk. 90012 90025 90004 Vascular causes: 90005 90010 90011 VRVMT – varicose venous system of the small pelvis. 90012 90011 Pelvic varicose veins – an increase in the length of the pelvic veins, their expansion. 90012 90025 90004 Musculoskeletal causes: 90005 90010 90011 Inflammatory processes in the joints. 90012 90011 Fibromyalgia is a muscle spasm that causes lower back pain. 90012 90025 90004 Gastrointestinal causes: 90005 90010 90011 Colitis 90012 90011 Retroperitoneal cancer process, tumors.90012 90011 Intestinal obstruction. 90012 90025 90004 Psychogenic causes – depressive disorders, violence, neurotic fear of sexual contact. 90005 90004 90055 [21], [22], [23], [24], [25], [26] 90005 90002 Sore lower abdomen to the left 90003 90004 The lower abdomen can be divided into quadrants – right side, umbilical, left side, right and left inguinal area and pubic part. Localization of pain in a particular area is one of the important diagnostic symptoms that help to identify the cause of pain.90005 90004 The lower abdominal pain on the left is a signal of possible problems in the organs located in this abdominal part: in the left part of the intestine, in the left kidney, in the internal reproductive organs. Also, pain in the left abdomen can be non-specific and identical in the diagnostic sense with pain in the right abdominal region, with the exception of inflammation of the appendix. If the lower abdomen is painful on the left, this may mean that the sigmoid colon has become inflamed, or urolithiasis, adnexitis or diverticulitis develops.In connection with the non-specificity of the left-sided pain symptom, the diagnosis includes a full examination of the abdominal organs, regardless of their location, on the right or on the left. A comprehensive study allows timely detection of diverticulitis, which is also called left-sided appendicitis. If this disease is not diagnosed on time, especially in elderly patients, it can lead to perforation of the lower part of the large intestine (sigmoid), which is an indication for urgent surgical intervention.Also, pain in the left quadrant of the abdomen can also manifest tubal pregnancy, besides, an ingress of inguinal hernia signals this way about itself. One of the causes of left-sided pain can be ulcerative colitis, granulomatous enteritis (Crohn’s disease or terminal ileitis), and worm infestation. Often the kidney calculus, which is located in the left kidney, passing the path to the bladder, also causes severe pain in the left side of the peritoneum. 90005 90004 90055 [27] 90005 90002 Sore lower right 90003 90004 Explicit localization of pain, in a sense, is a plus for diagnosing the disease, while diffuse (widespread) pain in the lower abdomen makes it difficult to make a diagnosis because of its non-specificity.The first thing that comes to mind with right-side abdominal pain is inflammation of the appendix. Indeed, the right-sided localization of painful sensations is a specific manifestation of appendicitis, but the lower abdomen hurts in the right way with other diseases. For example, an inflamed ureter or an attack of cholecystitis, an inflammation of the liver, or an acute stage of pyelonephritis can also be “responded” by right-sided painful sensations. It may also signal its development Crohn’s disease – a complex inflammatory disease of unknown etiology.Terminal ileitis, also called Crohn’s disease, is a pathological lesion of the walls of the entire digestive tract, starting from the iliac region, where the first symptoms appear. However, when ileitis develops, symptoms may move down the peritoneum. In addition, cystitis or urolithiasis, right ulcerative colitis, herpetic lesions of the intestinal walls can signal and manifest pain, localized in the lower right abdomen. 90005 90004 Since the abdomen is a container of a variety of organs and systems, right-sided pain may indicate an inflammatory process, pathology or a chronic course of the disease of the following organs located exactly in this part of the peritoneum: 90005 90010 90011 Worm-like area of the cecum or appendix, inflammation of which is most often manifested by pain in the right side of the abdomen – the upper or lower quadrant.90012 90011 Most of the intestinal tract, zones of which are often subjected to inflammation, including infectious nature, obstruction, and oncological process in the intestine is also possible. 90012 90011 In the right lower quadrant is the right ureter, which can be inflamed and manifest right-sided pain. 90012 90011 The right fallopian tube, which by the anatomical structure is slightly longer than the left. In the tube, inflammation may develop – salpingitis, endometrial polyp. 90012 90025 90004 90055 [28] 90005 90002 Sore lower stomach and fever 90003 90004 This is a signal that the pathological process in the peritoneal organs is already entering an acute stage.Hyperthermia is a characteristic symptom of an acute inflammatory disease, but this symptom often manifests itself at the stage when urgent medical care is needed. Even with gangrenous appendicitis, the patient may have a relatively low body temperature, and during perforation, it may even decrease. Also, hyperthermia itself can not be a specific symptom of a viral or bacterial infection. Many severe ulcerative processes are not always accompanied by significant temperature fluctuations, for example, a perforated ulcer is often only painful in the first few hours.90005 90004 Appendicitis, inflammation in the gallbladder (cholecystitis), diverticulitis, dysentery, adnexitis and pyelonephritis, many other diseases may be accompanied by painful sensations and slight hyperthermia. This applies to urological pathologies, gynecological and proctologic diseases, and even venereal diseases, since, for example, gonorrhea is also sometimes manifested by abdominal pain and hyperthermia. The combination of “low abdominal pain and temperature” in clinical practice is considered a serious signal of the acute period of the disease, and a high temperature that exceeds 38-39C is clear evidence of an septic lesion of the body, which can be caused by apoplexy of the ovarian cyst, rupture of the abdominal aorta, spleen infarction, peritonitis, rupture of the fallopian tube, infectious diseases of the kidneys or gall bladder.Both too high borderline temperatures and low temperatures – hypothermia – are bad signs in the prognostic sense. All conditions in the symptoms of which there is pain in the lower abdomen and temperature require medical help, and if the thermometer shows 34-35 or 38-40C, you need to call an ambulance, as this is a clear sign of sepsis and internal bleeding. 90005 90004 90055 [29], [30], [31] 90005 90002 Chronic lower abdominal pain 90003 90004 Chronic lower abdominal pain is a persistent pain that remains the main complaint that disrupts the ability to work for six months or more.The correlation between the severity of pain and the severity of abdominal pathology is usually insignificant. Chronic abdominal pain is often accompanied by mental disorders such as depression and sleep disorders. Chronic pain in the abdomen, not associated with diseases, most often occurs in women who have been sexually abused. There are also statistics that a third of women who underwent laparoscopy for chronic pain, could not find out the cause of the disease, which indicates the psychogenic cause of acute pain.10-20% of hysterectomy in the United States annually conduct about chronic lower abdominal pain, provoked by purely mental factors. Hysterectomy is highly effective in reducing the severity of pain syndromes associated with a subconscious protest against sexual contact. This reduces sexual dysfunction, reduces the level of psychogenia and improves the quality of life for a woman, even if there is no pathology on the part of the uterus. There is no data on the conduct of hysterectomy for psychogenic pains in our countries, it is obvious that such operations are not in demand and necessary for our women so far.The pain may also be the result of a latent inflammatory process, infectious diseases such as chlamydia or mycoplasmosis. Any discomfort associated with sexual relations should be eliminated, perhaps not in such a radical way as practiced in the United States. Modern gynecology has more effective means to help identify the true cause of pain after sex and effectively eliminate it. 90005 90004 90055 [32], [33], [34], [35], [36] 90005 90224 Chronic lower abdominal pain due to gynecological problems 90225 90004 Dysmenorrhea is the most common cause of chronic pain.Dysmenorrhea is a pain in the uterus that is cyclical in nature that occurs before or during menstruation. Primary dysmenorrhea is not believed to be associated with pathology of the pelvic organs, but with hyperproduction of prostaglandins in the uterus. Secondary dysmenorrhea is usually associated with the presence of acquired pathology (for example, endometriosis). 90005 90004 Endometriosis. The severity of pain in this disease varies from dysmenorrhea to intense non-inhibited chronic pain resulting in disability.The intensity of pain does not correlate with the severity of the pathology. 90005 90004 Adenomyosis is a common condition, most women are asymptomatic. Adenomyosis is characterized by an enlarged, softened uterus, slightly painful on palpation. However, adenomyosis is considered a pathological condition. 90005 90004 Fibromyoma is the most common benign tumor of the pelvic cavity in women. Fibromyoma pain is caused either by compression of adjacent organs, or by degenerative processes that occur in the tumor.90005 90004 Preserved ovarian syndrome is characterized by recurrent pain in the uterine appendages after hysterectomy. 90005 90004 The prolapse of the genitals may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness, pressure or dull pain. 90005 90004 Chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs are characterized by prolonged pain, usually due to the presence of hydrosalpinx, tubo-ovarian cyst or adhesions in the pelvic cavity. 90005 90004 90055 [37], [38], [39], [40], [41], [42] 90005 90224 Chronic lower abdominal pain due to non-gynecological diseases 90225 90004 Adhesions after infections or surgeries can cause chronic abdominal pain, difficult to treat.90005 90004 Pathology of the digestive tract, such as inflammatory diseases of the colon (Crohn’s disease ,, ulcerative colitis), irritable bowel syndrome, constipation, fecal blockages, may be accompanied by painful manifestations. Abdominal pain may worsen in the perimenstrual period. 90005 90004 Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, such as abnormal posture, muscle sprain and hernia between vertebral discs, can cause reflected pain. 90005 90004 90055 [43], [44] 90005.90000 Pain in Lower Right Abdomen: 16 Possible Causes 90001 90002 The lower right part of your abdomen is home to part of your colon and, for some women, the right ovary. There are many conditions that can cause you to feel mild to severe discomfort in your right abdominal region. More often than not, pain in the lower right abdomen is nothing to worry about and will go away on its own in a day or two. 90003 90002 But if you’re experiencing persistent discomfort, you should see your doctor. They can assess your symptoms and make a diagnosis.90003 90002 You should seek immediate medical attention if you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms: 90003 90008 90009 pain or pressure in your chest 90010 90009 fever 90010 90009 bloody stools 90010 90009 persistent nausea and vomiting 90010 90009 skin that appears yellow (jaundice) 90010 90009 severe tenderness when you touch your abdomen 90010 90009 swelling of the abdomen 90010 90023 90002 If you feel any of these symptoms, have someone drive you to the emergency room immediately.Urgent care can help prevent these symptoms from becoming severe or life-threatening. 90003 90002 Your appendix is a small, thin tube that’s located where the large and small intestines meet. When your appendix becomes inflamed, it’s known as appendicitis. Appendicitis is a common cause of pain specifically in the lower right abdomen. 90003 90002 Other symptoms of appendicitis can include: 90003 90002 The condition often requires immediate medical attention. So, if you’re experiencing these symptoms, you should see your doctor.After your doctor diagnoses the condition, they’ll either send you home with a treatment plan or admit you to the hospital for further observation. 90003 90002 Your doctor may determine that surgery to remove your appendix (appendectomy) is necessary to prevent the organ from rupturing and causing other complications. If your appendicitis is severe, your doctor may remove your appendix immediately. 90003 90002 If you’re experiencing symptoms of appendicitis, you should not take enemas or laxatives, as they can cause your appendix to burst.It’s best to avoid any type of medications unless they’re prescribed by your doctor as part of your treatment plan. 90003 90002 These causes are the most common reasons you may experience pain on either side of the lower abdomen. Although you may feel discomfort on the right side, this pain can also occur on your left. 90003 90038 Gas 90039 90002 Intestinal gas is air found in your entire digestive tract. It’s often caused by food that’s not broken down completely until it reaches your colon.90003 90002 The more undigested food present, the more gas your body will produce. As gas builds up, it can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and a “knotted” feeling in your stomach. 90003 90002 Burping and farting usually provide relief. In fact, it’s typical for a person to expel gas up to 20 times a day. 90003 90002 However, excessive gas may be a sign of a digestive disorder, such as diabetes or lactose intolerance. 90003 90002 Other causes for intestinal gas include: 90003 90008 90009 swallowing more air than normal 90010 90009 overeating 90010 90009 chewing gum 90010 90009 smoking 90010 90023 90038 Indigestion 90039 90002 Indigestion (dyspepsia) typically develops after you eat or drink something.Pain usually occurs in the upper abdomen, though it may still be felt lower down. 90003 90002 Symptoms of indigestion also include: 90003 90008 90009 heartburn 90010 90009 bloating 90010 90009 early or uncomfortable fullness 90010 90009 feeling sick 90010 90009 burping 90010 90009 farting 90010 90009 food or bitter-tasting fluids coming back up 90010 90023 90002 Mild indigestion will go away fairly quickly and can be treated by over-the-counter medications. But if symptoms persist for more than two weeks, you should see your doctor to rule out underlying digestive issues.90003 90038 Hernia 90039 90002 A hernia happens when a body part or internal organ pushes through tissue or muscle that holds it in place. There are several types of hernias, most of which happen in the abdomen. Each type can cause pain or discomfort in the affected area. 90003 90002 Other common symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 swelling or bulging at the site 90010 90009 increased pain 90010 90009 pain while lifting, laughing, crying, coughing, or straining 90010 90009 a dull ache 90010 90009 feeling full or constipated 90010 90023 90038 Kidney infection 90039 90002 A kidney infection is caused by bacteria that usually come from your bladder, ureters, or urethra.One or both of your kidneys could be affected by the infection. 90003 90002 Although you may feel pain in your lower abdomen, discomfort from a kidney infection more often occurs in your back, sides, or groin. 90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 fever 90010 90009 chills 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 frequent urination 90010 90009 feeling the need to urinate, even if you just went 90010 90009 pain or burning when urinating 90010 90009 pus or blood in your urine 90010 90009 urine that’s cloudy or smells bad 90010 90023 90002 When untreated, kidney infections can cause permanent damage.If you notice any of these symptoms, you should see your doctor right away. 90003 90038 Kidney stones 90039 90002 Kidney stones are a hard buildup of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. You may not feel any pain until the kidney stones begin to move around or pass into the tube that connects your kidney and bladder. 90003 90002 When this happens, you’ll feel severe pain in your back and side, below the ribs, and throughout your lower abdomen and groin. The intensity and location of the pain may change as the kidney stone shifts and moves through your urinary tract.90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 painful urination 90010 90009 pink, red, or brown urine 90010 90009 urine that’s cloudy or smells bad 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 feeling the constant need to pee 90010 90009 frequent urination 90010 90009 fevers and chills, if infection is also present 90010 90023 90038 Irritable bowel syndrome 90039 90002 Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common, chronic disorder that affects the large intestine. 90003 90002 IBS causes: 90003 90008 90009 cramps 90010 90009 bloating 90010 90009 gas 90010 90009 diarrhea 90010 90009 constipation 90010 90009 abdominal pain 90010 90009 a change in bowel movements 90010 90009 mucus in the stool 90010 90023 90002 Doctors do not know what causes irritable bowel syndrome, though some factors have been identified.This includes stronger-than-normal intestinal contractions or abnormalities in your digestive nervous system. 90003 90038 Inflammatory bowel disease 90039 90002 IBS should not be confused with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). IBD is a group of debilitating digestive disorders that cause changes in bowel tissue and increase your risk of colorectal cancer. 90003 90002 Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are the two most common causes of IBD. Both chronic conditions cause inflammation within your digestive tract, which can lead to abdominal pain.90003 90002 IBD may also cause: 90003 90008 90009 severe diarrhea 90010 90009 fatigue 90010 90009 weight loss 90010 90009 fever 90010 90009 blood in your stool 90010 90009 reduced appetite 90010 90023 90002 IBD can lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated. You should see your doctor immediately if you notice any of these symptoms. 90003 90002 Some causes of lower abdominal pain affect women only. These conditions are generally more serious and need medical attention. Although you may experience pain on the lower right side of your abdomen, this pain can also develop on the left side.90003 90038 Menstrual cramps 90039 90002 Menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) are a symptom of menstruation. They can happen before or during your period. The cramps are most often felt on either or both sides of the lower abdomen, which is where your uterus is contracting to get rid of its lining. 90003 90002 Other common symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 dull, constant ache 90010 90009 pain throughout your lower back and thighs 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90009 loose stools 90010 90009 headaches 90010 90009 dizziness 90010 90023 90038 Endometriosis 90039 90002 Although cramps are a common symptom of menstruation , they can also be caused by an underlying issue such as endometriosis.Endometriosis occurs when the lining that normally grows inside of your uterus forms on the outside of the organ. 90003 90002 In addition to severe cramps and lower abdominal pain, endometriosis can cause: 90003 90008 90009 pain during or after sex 90010 90009 painful bowel movements or peeing during menstruation 90010 90009 heavy periods 90010 90009 spotting or bleeding between periods 90010 90023 90002 It’s an agonizing and chronic condition for many women, and can lead to infertility.If you suspect endometriosis may be the reason for your abdominal pain, see your doctor. The sooner the condition can be treated, the less likely complications are. 90003 90038 Ovarian cyst 90039 90002 Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluid found on or inside the ovary. Most cysts do not cause pain or discomfort, and they may eventually disappear on their own. But a large ovarian cyst, especially if it’s ruptured, can lead to serious symptoms. 90003 90002 This includes: 90003 90008 90009 dull or sharp lower abdomen pain 90010 90009 bloating 90010 90009 full or heavy feeling in your abdomen 90010 90023 90002 You should see your doctor right away if these symptoms are accompanied by: 90003 90008 90009 sudden and severe abdominal pain 90010 90009 fever 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 cold and clammy skin 90010 90009 rapid breathing 90010 90009 weakness 90010 90023 90038 Ectopic pregnancy 90039 90002 An ectopic pregnancy happens when a fertilized egg implants itself in one of the fallopian tubes.90003 90002 In addition to abdominal pain, symptoms can include: 90003 90008 90009 vaginal bleeding 90010 90009 pain where your shoulder ends and your arm begins 90010 90009 painful peeing or bowel movements 90010 90009 diarrhea 90010 90023 90002 If the ectopic pregnancy ruptures, you may also experience: 90003 90002 These symptoms can intensify as the egg grows. 90003 90038 Pelvic inflammatory disease 90039 90002 Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is often caused by untreated sexually transmitted diseases.90003 90002 PID can cause pain in your lower abdomen, as well as: 90003 90008 90009 fever 90010 90009 unusual vaginal discharge with a bad odor 90010 90009 pain and bleeding during sex 90010 90009 burning during urination 90010 90009 bleeding during periods 90010 90023 90038 Ovarian torsion 90039 90002 Ovarian torsion happens when your ovary, and sometimes fallopian tube, becomes twisted, cutting off the organ’s blood supply. Also known as adnexal torsion, the condition can cause severe lower abdominal pain.90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 irregular periods 90010 90009 pain during sex 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 feeling full even though you’ve barely eaten 90010 90023 90002 Ovarian torsion often requires surgery to untwist the ovary. 90003 90002 Some causes of lower abdominal pain affect men only. These conditions are generally more serious and need medical attention. Although you may feel pain on the right side of your lower abdomen, this pain can also happen on your left side.90003 90038 Inguinal hernia 90039 90002 Inguinal hernia is one of the most common types of hernias. They are far more common in men than in women. It happens when fat or part of the small intestine pushes through a weak part of your lower abdomen. 90003 90002 If this happens, you’ll notice a small bulge in your groin area between your thigh and lower abdomen. You may also feel discomfort and pain when straining, lifting, coughing, or exercising. 90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 weakness, heaviness, aching, or burning in the groin 90010 90009 swollen or enlarged scrotum 90010 90023 90038 Testicular torsion 90039 90002 Testicular torsion happens when your testicle turns and twists the spermatic cord.This twisting causes reduced blood flow to the area, leading to sudden and severe pain and swelling in the scrotum. The condition also causes abdominal pain. 90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 nausea 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 uneven testicle position 90010 90009 painful urination 90010 90009 fever 90010 90023 90002 Testicular torsion usually requires emergency surgery. 90003 90002 You should make a doctor’s appointment if your lower right abdominal pain lasts more than a few days or causes you any concern.90003 90002 Mild cases of abdominal pain can usually be treated at home. For example, changing your diet can help treat gas and indigestion, while certain pain relievers can help control menstrual cramps. 90003 90002 Generally, though, you should avoid using aspirin (Bufferin) or ibuprofen (Advil) because they can irritate your stomach, worsening abdominal pain. 90003.90000 Pain in Lower Left Abdomen: 14 Causes 90001 90002 The lower left side of your abdomen is home to the last part of your colon, and for some women, the left ovary. Minor pain in this area is usually nothing to worry about and may clear up on its own in a day or two. 90003 90002 If you have pain related to an accident or injury, call your local emergency services right away. You should also seek immediate medical attention if you feel pressure or pain in your chest. 90003 90002 Ask someone to help you get to urgent care or an emergency room if you have: 90003 90008 90009 fever 90010 90009 severe tenderness in the affected area 90010 90009 swelling of the abdomen 90010 90009 bloody stools 90010 90009 persistent nausea and vomiting 90010 90009 unexplained weight loss 90010 90009 skin that looks yellow (jaundice) 90010 90023 90002 Read on to learn more about pain in the lower left abdomen, what causes it, and when to see your doctor.90003 90002 In many cases, persistent pain specific to the lower left side of the abdomen is caused by diverticulitis. 90003 90002 Diverticula are small pouches created from pressure on weak spots in the colon. Diverticula are common, and even more so after age 40. When a pouch tears, swelling and infection can cause diverticulitis. 90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 fever 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 abdominal tenderness 90010 90023 90002 Less commonly, constipation or diarrhea can be a sign of diverticulitis.90003 90002 For mild diverticulitis, most people respond well to rest, a change in diet, and antibiotics. Some people need surgery if the condition is severe or continues to return. 90003 90002 Here are some of the most common reasons for pain on either side of the lower abdomen. 90003 90048 90049 Gas 90050 90051 90002 Passing gas and belching are normal. Gas can be found throughout your digestive tract, from your stomach to your rectum. Gas is the normal result of swallowing and digestion.90003 90002 Gas can be caused by: 90003 90008 90009 swallowing more air than usual 90010 90009 overeating 90010 90009 smoking 90010 90009 chewing gum 90010 90009 being unable to fully digest some foods 90010 90009 eating gas-producing foods 90010 90009 having a disruption of the bacteria in the colon 90010 90023 90002 Gas usually is not serious. Talk with your doctor if it’s persistent or goes along with other symptoms, such as: 90003 90008 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 diarrhea 90010 90009 constipation 90010 90009 unintentional weight loss 90010 90009 heartburn 90010 90009 blood in the stool 90010 90023 90002 Shop online for gas relief medications .90003 90048 90049 Indigestion 90050 90051 90002 Indigestion usually happens after eating. Your stomach makes acid when you eat. This acid can irritate your esophagus, stomach, or bowel. The pain is usually in the upper part of the abdomen but in rare cases may also affect the lower abdomen. 90003 90002 Indigestion is usually mild, and most people have had the discomfort, pain, or burning sensation that can go along with it. 90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 heartburn 90010 90009 feeling full or bloated 90010 90009 belching or passing gas 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90023 90002 See your doctor if indigestion continues or worsens.90003 90002 Shop online for antacids. 90003 90048 90049 Hernia 90050 90051 90002 A hernia is the result of an internal organ or other body part pushing through the muscle or tissue surrounding it. A lump or bulge may appear with some hernias in the abdomen or groin. 90003 90002 Other symptoms may include: 90003 90008 90009 increasing size of the bulge 90010 90009 increasing pain at the site 90010 90009 pain when lifting 90010 90009 a dull ache 90010 90009 a feeling of fullness 90010 90023 90002 Different symptoms go along with each type of hernia .For example, hiatal hernias do not produce a bulge. 90003 90002 The specific cause depends on the type of hernia. Hernias may cause serious problems, so see your doctor if you suspect that you may have one. 90003 90048 90049 Kidney stones 90050 90051 90002 A kidney stone usually starts to cause problems when it moves around inside your kidney or into your ureter, the tube that connects the kidney to the bladder. 90003 90002 The stone may then cause severe pain in the side and back, under your ribs.The pain may also come in waves and get better or worse from one moment to the next, as the stone moves through your urinary tract. 90003 90002 You may also experience: 90003 90008 90009 urine that is pink, red, brown, cloudy, or smelly 90010 90009 urination that is painful or happening more often 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 fever or chills 90010 90023 90002 There is no single cause of a kidney stone. Some things may increase your risk, like someone in your family having a stone.See your doctor if you have symptoms that worry you. 90003 90048 90049 Shingles 90050 90051 90002 Ever had the chickenpox? If so, the varicella-zoster virus sits quietly in your body. The virus can show up again later as shingles. Your risk goes up as you age, usually after age 50. 90003 90002 The shingles infection can cause a painful rash that looks like a stripe of blisters wrapping around one side of your body. Sometimes the rash shows up on the neck or face. Some people have pain but no rash.90003 90002 Other symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 burning, numbness, or tingling 90010 90009 sensitivity to touch 90010 90009 blisters that break open and form scabs 90010 90009 itching 90010 90023 90002 The shingles vaccine can help lower your chances of getting shingles. If you do get shingles, see your doctor. Starting treatment early can shorten the infection and lower your chances of having other problems. 90003 90002 Some causes of lower left abdominal pain only affect women. These conditions may be more serious or need medical attention.Pain can also develop on right side of your abdomen in these cases. 90003 90048 90049 Menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) 90050 90051 90002 Cramps usually occur before and during your menstrual period. Although the pain can range from a minor annoyance to something that interferes with your daily activities, menstrual cramps usually are not serious. 90003 90002 See your doctor if: 90003 90008 90009 your cramps interfere with your daily activities 90010 90009 your symptoms get worse over time 90010 90009 you’re older than age 25 and your cramps have started to get more severe 90010 90023 90048 90049 Endometriosis 90050 90051 90002 With endometriosis, tissue that typically lines the inside of your uterus also grows outside of the uterus.This can cause abdominal pain and lead to infertility. 90003 90002 Some other symptoms are: 90003 90008 90009 painful menstrual cramps that may get worse with time 90010 90009 pain with sex 90010 90009 painful bowel movements or urination 90010 90009 heavy menstrual periods 90010 90009 spotting between periods 90010 90023 90002 The cause of endometriosis is unknown . It’s time to see your doctor when your symptoms are severe and interfere with your daily activities. 90003 90048 90049 Ovarian cyst 90050 90051 90002 An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid inside or on the surface of an ovary.These are part of a woman’s normal menstrual cycle. 90003 90002 Most cysts do not produce symptoms and go away without treatment in a few months. A large cyst can cause discomfort. It may also press on your bladder and cause you to urinate more often. 90003 90002 A cyst that ruptures (breaks open) can cause some serious problems, such as severe pain or internal bleeding. 90003 90002 See your doctor or get medical help right away if you’re experiencing: 90003 90008 90009 sudden, severe abdominal pain 90010 90009 pain with fever or vomiting 90010 90009 signs of shock, such as cold and clammy skin, rapid breathing, lightheadedness, or weakness 90010 90023 90048 90049 Ovarian torsion 90050 90051 90002 Large ovarian cysts may cause the ovary to change position in a woman’s body.This raises the risk of ovarian torsion, a painful twisting of the ovary that can cut off blood supply. The fallopian tubes may also be affected. 90003 90002 Ovarian torsion is more likely to happen with pregnancy or the use of hormones to promote ovulation. 90003 90002 Ovarian torsion is not common. When it does happen, it’s usually during a woman’s reproductive years. See your doctor if you feel a sudden severe pain in your abdomen with vomiting. Surgery is often needed to untwist the ovary or remove it.90003 90048 90049 Ectopic pregnancy 90050 90051 90002 With ectopic pregnancy, a fertilized egg implants itself before it reaches the uterus. This usually happens inside the fallopian tubes connecting the ovary to the uterus. You may or may not have symptoms with an ectopic pregnancy. 90003 90002 In addition to abdominal pain, symptoms can include: 90003 90008 90009 a missed period and other pregnancy signs 90010 90009 vaginal bleeding 90010 90009 watery discharge 90010 90009 discomfort with urination or bowel movements 90010 90009 shoulder pain at the tip 90010 90023 90002 See your doctor if you have these symptoms and you believe you may be pregnant, even if your pregnancy test is negative and it’s still very early.90003 90002 An ectopic pregnancy that ruptures (breaks open) is serious and needs surgery to repair the fallopian tube. Get medical help right away if you’re: 90003 90008 90009 feeling sick or dizzy 90010 90009 feeling faint 90010 90009 looking very pale 90010 90023 90048 90049 Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) 90050 90051 90002 PID is an infection of the reproduction system in women. It’s commonly caused by sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, but other types of infections can also lead to PID.90003 90002 You may or may not have symptoms with PID. 90003 90002 In addition to abdominal pain, symptoms can include: 90003 90008 90009 fever 90010 90009 vaginal discharge with a bad odor 90010 90009 pain or bleeding with sex 90010 90009 a burning sensation with urination 90010 90009 bleeding between periods 90010 90023 90002 See your doctor if you think you or your partner have been exposed to an STD or if you have any genital symptoms, such as an unusual sore or discharge. 90003 90002 Some causes of lower left abdominal pain only affect men.These conditions may be more serious or need medical attention. Pain can also develop on the right side of the abdomen in these cases. 90003 90048 90049 Inguinal hernia 90050 90051 90002 An inguinal hernia is the result of fat or a portion of the small intestine pushing through a weak area in a man’s lower abdomen. This type of hernia is much less common in women. 90003 90002 Some symptoms are: 90003 90008 90009 a small bulge on the side of the groin that may get larger over time and usually goes away when you lay down 90010 90009 pain in the groin that gets worse when straining, lifting, coughing, or during physical activity 90010 90009 weakness, heaviness, burning, or aching in the groin 90010 90009 a swollen or enlarged scrotum 90010 90023 90002 This type of hernia can cause serious problems.Get medical help right away if you have: 90003 90008 90009 extreme tenderness or redness at the bulge site 90010 90009 sudden pain that gets worse and continues 90010 90009 problems passing gas or having a bowel movement 90010 90009 nausea and vomiting 90010 90009 fever 90010 90023 90048 90049 testicular torsion 90050 90051 90002 In testicular torsion, the testicle rotates. This lowers blood flow to the testicles and causes severe pain and swelling. The cause of this condition is unknown.Testicular torsion can happen in any male, but it occurs most often in boys aged 12 to 16. 90003 90002 Some symptoms include: 90003 90008 90009 sudden, severe scrotum pain and swelling 90010 90009 abdominal pain 90010 90009 nausea 90010 90009 vomiting 90010 90009 painful urination 90010 90009 fever 90010 90023 90002 Testicular torsion is very serious. Get medical help right away if you have sudden or severe pain in your testicles. If the pain goes away on its own, you still need to see your doctor right away.Surgery may prevent damage to the testicle and preserve your ability to have children. 90003 90002 Are you worried about your abdominal pain? Has it lasted more than a few days? If you answered yes to both questions, it’s time to see your doctor. If you do not already have a provider, our Healthline FindCare tool can help you connect to physicians in your area. 90003 90002 Until then, pay attention to your pain and see if anything eases it. The bottom line? Listen to your body and see your doctor sooner rather than later if the pain persists.90003 90002 Healthline and our partners may receive a portion of revenues if you make a purchase using a link above. 90003.90000 Pain in lower left abdomen: 12 possible causes 90001 90002 There are several possible causes of lower left abdomen pain. Some causes are more common and benign, while others can be serious and require medical attention. 90003 90004 1. Diverticulitis 90005 90002 Diverticulitis is one of the most common causes of lower left abdominal pain. Diverticulitis occurs when diverticula (small pouches) in the intestinal wall become infected and inflamed. 90003 90002 Diverticula form in weak areas of the large intestine, which is often referred to as the colon.90003 90002 Diverticula are present in many adults. As a person ages, the number of diverticula increases, making it more likely that one will tear or swell. As a result, diverticulitis tends to be more common in older adults, although younger people can still develop the condition. 90003 90002 Diverticulitis pain tends to increase while a person is eating or shortly after a meal. 90003 90002 Additional symptoms of diverticulitis may include: 90003 90016 90017 tenderness in the abdomen 90018 90017 fever 90018 90017 nausea 90018 90017 vomiting 90018 90017 feeling bloated 90018 90027 90004 2.Celiac disease 90005 90002 Celiac disease is a chronic condition that occurs in the digestive tract when a person can not digest gluten. Gluten is a protein found in wheat and is present in several foods and healthcare products. 90003 90002 When a person has celiac disease, their immune system attacks portions of the intestine, causing a range of digestive problems and vitamin deficiencies. 90003 90002 Symptoms of celiac disease may include: 90003 90002 Children with undiagnosed celiac disease may also suffer from malnourishment and growth impediments as a result of the condition.90003 90004 3. Gas 90005 90002 Gas is often trapped in the digestive tract when a person swallows air while eating, as well as through natural digestion processes. 90003 90002 Typically, gas is not anything to worry about and will pass through either the rectum or esophagus. Gas that is temporarily trapped in the digestive tract can cause pain and discomfort until it moves out of the system. 90003 90002 Gas can be caused by: 90003 90016 90017 digesting foods that are prone to releasing gas 90018 90017 swallowing air 90018 90017 smoking 90018 90017 chewing gum 90018 90017 overeating 90018 90017 undigested foods 90018 90017 bacteria 90018 90027 90002 If the gas pain is frequent or accompanied by additional symptoms, a person may wish to speak to a doctor.Other symptoms include: 90003 90004 4. Lactose intolerance 90005 90002 A person who is lactose intolerant has trouble digesting milk and milk-based products, such as cheese and yogurt. This is because the person lacks sufficient amounts of an enzyme called lactase. 90003 90002 Lactase breaks down the lactose in milk, which consists of the simple sugars glucose and galactose. 90003 90002 When a person has high levels of lactose in their bloodstream, they may develop symptoms associated with lactose intolerance.These symptoms include: 90003 90016 90017 loose stool or diarrhea 90018 90017 pain in the abdomen 90018 90017 bloating 90018 90017 gas pain 90018 90017 nausea 90018 90017 a growling or rumbling stomach 90018 90027 90004 5. Inflammatory bowel diseases 90005 90002 Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are chronic conditions that can cause painful inflammation anywhere in the digestive tract. 90003 90002 Crohn’s disease is most common in the small intestine, and ulcerative colitis is most common in the colon.90003 90002 It is still not known what causes Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. The most common symptoms include pain in the abdomen and bloody diarrhea. It can also cause fever and unexplainable weight loss. 90003 90004 6. Indigestion 90005 90002 Indigestion is caused by a buildup of acid after eating. For most people, indigestion pain occurs in the upper part of the abdomen. While rare, indigestion can occur in the lower part of the abdomen. 90003 90002 Typically, most cases of indigestion are mild.Symptoms of indigestion include a burning sensation, slight pain or discomfort, heartburn, bloating, or gas. 90003 90002 There is an excellent selection of indigestion relief products that may be purchased online with thousands of customer reviews. 90003 90004 7. Shingles 90005 90002 Shingles is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. Once a person has had chickenpox, the virus stays dormant in the body for their entire life. Sometimes, the virus reappears, causing pain and a rash that wraps around one side of the abdomen.90003 90002 Vaccines are available to help reduce the risk of a person developing the disease later in life. 90003 90002 Symptoms of shingles include: 90003 90016 90017 pain when touched 90018 90017 itching 90018 90017 tenderness on the skin 90018 90017 rash 90018 90017 blisters that may break open and scar 90018 90027 90002 A person may feel tenderness and itchiness on one area of the skin before the rash appears. They may also experience a fever or general malaise. Once the rash appears, the pain can be severe.90003 90004 8. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) 90005 90002 Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that a doctor may only diagnose once they have ruled out other probable causes of a person’s symptoms. 90003 90002 Symptoms of IBS may include: 90003 90016 90017 abdominal pain 90018 90017 pressure 90018 90017 constipation or diarrhea 90018 90017 gas 90018 90017 bloating 90018 90027 90004 9. Hernia 90005 90002 A hernia occurs when an organ or other body part pushes through the abdominal wall .Sometimes, a lump may appear in the midsection or near the groin. 90003 90002 Different types of hernias can occur, and they vary according to the underlying cause. Because hernias can cause additional problems, it is essential to see a doctor as soon as possible. 90003 90002 Some additional symptoms of hernia complications include: 90003 90016 90017 pain when lifting an object 90018 90017 pressure 90018 90017 increasing pain 90018 90017 increasing size of a bulge 90018 90017 a general feeling of fullness 90018 90027 90004 10.Constipation 90005 90002 Constipation occurs when a person can not pass a stool. It is often caused by poor diet and lack of exercise. Improving diet and increasing exercise are two of the most effective treatments. 90003 90002 Some symptoms of constipation include: 90003 90016 90017 straining when passing stool 90018 90017 needing to apply pressure to the abdomen to help push out a stool 90018 90017 a lumpy or very hard stool 90018 90017 feeling like the rectum is blocked 90018 90017 feeling like not all the stool has passed 90018 90017 having fewer than three bowel movements in a week 90018 90027 90004 11.Kidney stones 90005 90002 Most stones are formed from calcium buildup and can form in either the right or left kidney. 90003 90002 A person may develop a kidney stone and not realize they have it until the stone causes problems, such as blocking part of the kidney or causing great pain as it passes. 90003 90002 Typical symptoms of kidney stones include: 90003 90016 90017 abdominal pain 90018 90017 pain when urinating 90018 90017 nausea or vomiting 90018 90017 blood in the urine 90018 90017 fever 90018 90017 frequent urination 90018 90027 90004 12.Intestinal obstruction 90005 90002 When a blockage occurs in the intestine, food can not pass through the digestive tract. This results in a painful back-up that needs immediate medical attention. 90003 90002 Intestinal obstructions are more common in older adults and are typically caused by other conditions, such as diverticulitis or colon cancer. 90003 90002 Common symptoms of an intestinal obstruction include: 90003 90016 90017 abdominal pain 90018 90017 inability to pass stool 90018 90017 distention 90018 90017 vomiting 90018 90017 constipation 90018 90027 90002 The type of treatment will depend on the condition or disease causing the pain.90003 90002 Lower abdominal pain due to an infection, such as diverticulitis, will often only require antibiotics and resting as treatment. 90003 90002 Other, more structural problems, such as a hernia or an intestinal blockage, may require surgery. 90003 90002 Treatment for constipation and gas often includes basic dietary adjustments and, in severe cases, the use of laxatives. For more chronic lower abdominal pain, such as the pain in IBS or Crohn’s, more careful, long-term dietary management can help to manage symptoms.90003 90002 Treatment for food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance, often involves excluding that food from the diet. 90003.





